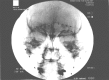
Concordant occipital and supraorbital neurostimulation therapy for hemiplegic migraine; initial experience; a case series
- PMID: 25688595
- PMCID: PMC5024009
- DOI: 10.1111/ner.12267
Concordant occipital and supraorbital neurostimulation therapy for hemiplegic migraine; initial experience; a case series
Abstract
Introduction: Hemiplegic migraine is a particularly severe form of the disease that often evolves to a debilitating chronic illness that is resistant to commonly available therapies. Peripheral neurostimulation has been found to be a beneficial therapy for some patients among several diagnostic classes of migraine, but its potential has not been specifically evaluated for hemiplegic migraine.
Materials and methods: Four patients with hemiplegic migraine were treated with concordant, combined occipital and supraorbital neurostimulation over periods ranging 6-92 months. The clinical indicators followed included assessments of headache frequency and severity, frequency of hemiplegic episodes, functional impairment, medication usage, and patient satisfaction.
Results: All reported a positive therapeutic response, as their average headache frequency decreased by 92% (30 to 2.5 headache days/month); Visual Analog Score by 44% (9.5 to 5.3); frequency of hemiplegic episodes by 96% (7.5 to 0.25 hemiplegic episodes/month); headache medication usage by 96% (6 to 0.25 daily medications); and Migraine Disability Assessment score by 98% (249 to 6). All were satisfied and would recommend the therapy, and all preferred combined occipital-supraorbital neurostimulation to occipital neurostimulation alone.
Conclusions: Concordant combined occipital and supraorbital neurostimulation may provide effective therapy for both the pain and motor aura in some patients with hemiplegic migraine.
Keywords: Chronic migraine; combined occipital and supraorbital nerve stimulation; hemiplegic migraine; migraine; occipital nerve stimulation.
© 2015 The Authors. Neuromodulation published by Wiley Periodicals, Inc. on behalf of International Neuromodulation Society.
Figures
References
-
- Headache Classification Subcommittee of the International Headache S . The international classification of headache disorders: 2nd edition. Cephalalgia 2004;24 (Suppl. 1):9–160. - PubMed
-
- Russell MB, Ducros A. Sporadic and familial hemiplegic migraine: pathophysiological mechanisms, clinical characteristics, diagnosis, and management. Lancet Neurol 2011;10:457–470. - PubMed
-
- Thomsen LL, Eriksen MK, Roemer SF, Andersen I, Olesen J, Russell MB. A population‐based study of familial hemiplegic migraine suggests revised diagnostic criteria. Brain 2002;125:1379–1391. - PubMed
-
- Thomsen LL, Ostergaard E, Olesen J, Russell MB. Evidence for a separate type of migraine with aura Sporadic hemiplegic migraine. Neurology 2003;60:595–601. - PubMed
-
- de Vries B, Frants RR, Ferrari MD, van den Maagdenberg AM. Molecular genetics of migraine. Hum Genet 2009;126:115–132. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous