The effects of Jieduquyuzishen prescription-treated rat serum on the BAFF/BAFF-R signal pathway
- PMID: 25689512
- PMCID: PMC4331425
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0118462
The effects of Jieduquyuzishen prescription-treated rat serum on the BAFF/BAFF-R signal pathway
Abstract
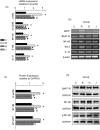
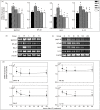
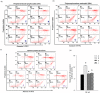
Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) is a chronic inflammatory disease mainly characterized by B cell hyperactivity. Glucocorticoid (GC) is widely used in SLE for its potent anti-inflammatory and immunosuppressive effects. Despite its important clinical efficacy, high-dose or long-term use of GC can cause severe side effects, such as osteoporosis, osteonecrosis, cataracts, hyperglycemia, coronary heart disease and cognitive impairment. Our early clinical studies have shown that Jieduquyuzishen prescription (JP) can effectively reduce the adverse effects and improve the curative effect of GC in the treatment of SLE. The BAFF/BAFF-R signaling pathway plays an important role in the development of SLE and has been regarded as a potential target for the therapy of SLE. In this study, we attempt to investigate the effect of JP on the BAFF/BAFF-R signaling pathway to explore the mechanism of JP in reducing the toxicity and enhancing the efficacy of GC. YAC-1 cells, isolated rat peripheral blood lymphocytes, polymorphonuclear neutrophils and spleen lymphocytes were treated with drug-containing serum. The results of RT-PCR, Western blot and dual-luciferase reporter gene assays indicate that either JP or GC can inhibit the mBAFF-induced up-regulation of BAFF, BAFF-R, Bcl-2, IL-10 and NF-κB in YAC-1 cells and WEHI-231 cells. Furthermore, MTS, flow cytometry and CFSE results reveal that the proliferation and survival of lymphocytes activated by mBAFF are suppressed by JP, GC and their combination. Contrary to GC, JP can reduce the apoptosis and raise the survival of polymorphonuclear neutrophils and can't increase the apoptosis of the peripheral blood lymphocytes and spleen lymphocytes. Therefore, it is possible that JP can down-regulate the BAFF/BAFF-R signaling pathway as effectively as GC, which may result in the dosage reduction of GC, thus decreasing the toxicity and improving the efficacy of GC-based treatment of SLE.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Similar articles
-
Expression of BAFF and BR3 in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus.Braz J Med Biol Res. 2016 Mar;49(3):e4853. doi: 10.1590/1414-431X20154853. Epub 2016 Feb 2. Braz J Med Biol Res. 2016. PMID: 26840704 Free PMC article.
-
Expression of B-cell activating factor of the tumour necrosis factor family (BAFF) in T cells in active systemic lupus erythematosus: the role of BAFF in T cell-dependent B cell pathogenic autoantibody production.Rheumatology (Oxford). 2007 Jul;46(7):1083-6. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/kem097. Epub 2007 May 11. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2007. PMID: 17500077
-
Investigations of a rabbit (Oryctolagus cuniculus) model of systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), BAFF and its receptors.PLoS One. 2009 Dec 30;4(12):e8494. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0008494. PLoS One. 2009. PMID: 20041151 Free PMC article.
-
Roles of TRAFs in NF-κB signaling pathways mediated by BAFF.Immunol Lett. 2018 Apr;196:113-118. doi: 10.1016/j.imlet.2018.01.010. Epub 2018 Feb 20. Immunol Lett. 2018. PMID: 29378215 Review.
-
BAFF and BAFF-Receptor in B Cell Selection and Survival.Front Immunol. 2018 Oct 8;9:2285. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.02285. eCollection 2018. Front Immunol. 2018. PMID: 30349534 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Effect of Jieduquyuziyin prescription-treated rat serum on MeCP2 gene expression in Jurkat T cells.In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim. 2018 Dec;54(10):692-704. doi: 10.1007/s11626-018-0295-x. Epub 2018 Oct 26. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim. 2018. PMID: 30367366
-
Jieduquyuziyin Prescription-Treated Rat Serum Suppresses Activation of Peritoneal Macrophages in MRL/Lpr Lupus Mice by Inhibiting IRAK1 Signaling Pathway.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2019 Nov 3;2019:2357217. doi: 10.1155/2019/2357217. eCollection 2019. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2019. PMID: 31781262 Free PMC article.
-
Sijunzi decoction-treated rat serum induces apoptosis of side population cells in gastric carcinoma.Exp Ther Med. 2018 Feb;15(2):1718-1727. doi: 10.3892/etm.2017.5560. Epub 2017 Nov 24. Exp Ther Med. 2018. PMID: 29399136 Free PMC article.
-
Traditional Chinese medicine for lupus nephritis: modulation of autoimmune pathogenesis.Front Pharmacol. 2025 May 2;16:1523272. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1523272. eCollection 2025. Front Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40385489 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pharmacological Mechanism of Chinese Medicine in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: A Narrative Review.Chin J Integr Med. 2025 Feb;31(2):157-169. doi: 10.1007/s11655-024-3762-0. Epub 2024 Sep 5. Chin J Integr Med. 2025. PMID: 39240290 Review.
References
-
- D’Cruz DP, Khamashta MA, Hughes GR. Systemic lupus erythematosus. Lancet. 2007; 369: 587–596. - PubMed
-
- Mills JA. Systemic lupus erythematosus. N Engl J Med. 1994; 330: 1871–1879. - PubMed
-
- Davidson A, Aranow C. Pathogenesis and treatment of systemic lupus erythematosus nephritis. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2006; 18: 468–475. - PubMed
-
- Isenberg DA, Rahman A, Allen E, Farewell V, Akil M, Bruce IN, et al. BILAG 2004. Development and initial validation of an updated version of the British Isles Lupus Assessment Group’s disease activity index for patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Rheumatology. 2005; 44: 902–906. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

