Modeling chemotherapeutic neurotoxicity with human induced pluripotent stem cell-derived neuronal cells
- PMID: 25689802
- PMCID: PMC4331516
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0118020
Modeling chemotherapeutic neurotoxicity with human induced pluripotent stem cell-derived neuronal cells
Abstract
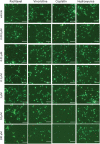
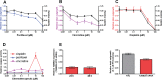
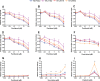
There are no effective agents to prevent or treat chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy (CIPN), the most common non-hematologic toxicity of chemotherapy. Therefore, we sought to evaluate the utility of human neuron-like cells derived from induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) as a means to study CIPN. We used high content imaging measurements of neurite outgrowth phenotypes to compare the changes that occur to iPSC-derived neuronal cells among drugs and among individuals in response to several classes of chemotherapeutics. Upon treatment of these neuronal cells with the neurotoxic drug paclitaxel, vincristine or cisplatin, we identified significant differences in five morphological phenotypes among drugs, including total outgrowth, mean/median/maximum process length, and mean outgrowth intensity (P < 0.05). The differences in damage among drugs reflect differences in their mechanisms of action and clinical CIPN manifestations. We show the potential of the model for gene perturbation studies by demonstrating decreased expression of TUBB2A results in significantly increased sensitivity of neurons to paclitaxel (0.23 ± 0.06 decrease in total neurite outgrowth, P = 0.011). The variance in several neurite outgrowth and apoptotic phenotypes upon treatment with one of the neurotoxic drugs is significantly greater between than within neurons derived from four different individuals (P < 0.05), demonstrating the potential of iPSC-derived neurons as a genetically diverse model for CIPN. The human neuron model will allow both for mechanistic studies of specific genes and genetic variants discovered in clinical studies and for screening of new drugs to prevent or treat CIPN.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Similar articles
-
Chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy models constructed from human induced pluripotent stem cells and directly converted cells: a systematic review.Pain. 2024 Sep 1;165(9):1914-1925. doi: 10.1097/j.pain.0000000000003193. Epub 2024 Feb 21. Pain. 2024. PMID: 38381959 Free PMC article.
-
Application of stem cell derived neuronal cells to evaluate neurotoxic chemotherapy.Stem Cell Res. 2017 Jul;22:79-88. doi: 10.1016/j.scr.2017.06.006. Epub 2017 Jun 15. Stem Cell Res. 2017. PMID: 28645005 Free PMC article.
-
Modeling mechanisms of chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy and chemotherapy transport using induced pluripotent stem cell-derived sensory neurons.Neuropharmacology. 2024 Nov 1;258:110062. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2024.110062. Epub 2024 Jul 5. Neuropharmacology. 2024. PMID: 38972371
-
Utilization of iPSC-derived human neurons for high-throughput drug-induced peripheral neuropathy screening.Toxicol In Vitro. 2017 Dec;45(Pt 1):111-118. doi: 10.1016/j.tiv.2017.08.014. Epub 2017 Aug 24. Toxicol In Vitro. 2017. PMID: 28843493
-
Bridging the Translational Gap in Chemotherapy-Induced Peripheral Neuropathy with iPSC-Based Modeling.Cancers (Basel). 2022 Aug 15;14(16):3939. doi: 10.3390/cancers14163939. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36010931 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Modeling chemotherapy induced peripheral neuropathy (CIPN) in vitro: Prospects and limitations.Exp Neurol. 2020 Apr;326:113140. doi: 10.1016/j.expneurol.2019.113140. Epub 2019 Dec 5. Exp Neurol. 2020. PMID: 31812556 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Bortezomib-induced neurotoxicity in human neurons is the consequence of nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide depletion.Dis Model Mech. 2022 Dec 1;15(12):dmm049358. doi: 10.1242/dmm.049358. Epub 2022 Dec 8. Dis Model Mech. 2022. PMID: 36398590 Free PMC article.
-
Human Induced Pluripotent Stem Cell Derived Sensory Neurons are Sensitive to the Neurotoxic Effects of Paclitaxel.Clin Transl Sci. 2021 Mar;14(2):568-581. doi: 10.1111/cts.12912. Epub 2020 Dec 19. Clin Transl Sci. 2021. PMID: 33340242 Free PMC article.
-
Chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy models constructed from human induced pluripotent stem cells and directly converted cells: a systematic review.Pain. 2024 Sep 1;165(9):1914-1925. doi: 10.1097/j.pain.0000000000003193. Epub 2024 Feb 21. Pain. 2024. PMID: 38381959 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of small molecules that mitigate vincristine-induced neurotoxicity while sensitizing leukemia cells to vincristine.Clin Transl Sci. 2021 Jul;14(4):1490-1504. doi: 10.1111/cts.13012. Epub 2021 May 31. Clin Transl Sci. 2021. PMID: 33742760 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

