Surveillance of hepatitis E virus contamination in shellfish in China
- PMID: 25689991
- PMCID: PMC4344708
- DOI: 10.3390/ijerph120202026
Surveillance of hepatitis E virus contamination in shellfish in China
Abstract
Background: Hepatitis E virus (HEV) has been confirmed to be a zoonotic virus of worldwide distribution. HEV contamination in the water environment has not been well examined in China. The objective of this study was to evaluate HEV contamination in shellfish in a coastal area of China. Such contamination would be significant for evaluating public health risks.
Methods: samples of three species shellfish were collected from thirteen points of estuarine tidal flats around the Bohai Gulf and screened for HEV RNA using an in-house nested RT-PCR assay. The detected HEV-positive samples were further verified by gene cloning and sequencing analysis.
Results: the overall HEV-positive detection rate is approximately 17.5% per kilogram of shellfish. HEV was more common among S. subcrenata (28.2%), followed by A. granosa (14.3%) and R. philippinarum (11.5%). The phylogenetic analysis of the 13 HEV strains detected revealed that gene fragments fell into two known 4 sub-genotypes (4b/4d) groups and another unknown group.
Conclusions: 13 different sub-genotype 4 HEVs were found in contaminated shellfish in the Bohai Gulf rim. The findings suggest that a health risk may exist for users of waters in the Bonhai area and to consumers of shellfish. Further research is needed to assess the sources and infectivity of HEV in these settings, and to evaluate additional shellfish harvesting areas.
Figures
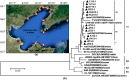
 and that of negative detection’s with a only a red circle
and that of negative detection’s with a only a red circle  . (b) Phylogenetic trees of hepatitis E virus (HEV) were constructed based on partial genomes. Each partial ORF3 (287basepairs) of 13 different clones of JZ12-1, JZ12-2, HLD12-1, HLD12-2, PJ12-1, DY12-1, SZ12-1, JZ13-1, JZ13-2, TJ13-1, TJ13-2, YK13-1and JZ13-3 (with GenBank accession No. KJ816338, KJ816339, KJ816336, KJ816337, KJ816343, KJ816335, KJ816344, KJ816340, KJ816341, KJ816345, KJ816346, KJ816347 and KJ816342, respectively.) was analyzed by the neighbor-joining method. The bootstrap value correspond to 1,000 replications of avian HEV was used as an outgroup. All nucleotide sequences determined in this study were marked by ▲. Other HEV sequences were retrived from GenBank.
. (b) Phylogenetic trees of hepatitis E virus (HEV) were constructed based on partial genomes. Each partial ORF3 (287basepairs) of 13 different clones of JZ12-1, JZ12-2, HLD12-1, HLD12-2, PJ12-1, DY12-1, SZ12-1, JZ13-1, JZ13-2, TJ13-1, TJ13-2, YK13-1and JZ13-3 (with GenBank accession No. KJ816338, KJ816339, KJ816336, KJ816337, KJ816343, KJ816335, KJ816344, KJ816340, KJ816341, KJ816345, KJ816346, KJ816347 and KJ816342, respectively.) was analyzed by the neighbor-joining method. The bootstrap value correspond to 1,000 replications of avian HEV was used as an outgroup. All nucleotide sequences determined in this study were marked by ▲. Other HEV sequences were retrived from GenBank.
Similar articles
-
Development and evaluation of a RT-LAMP assay for rapid detection of hepatitis E virus from shellfish.Int J Food Microbiol. 2016 Mar 2;220:1-5. doi: 10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2015.12.008. Epub 2015 Dec 23. Int J Food Microbiol. 2016. PMID: 26741532
-
Detection of Hepatitis E Virus in Shellfish Harvesting Areas from Galicia (Northwestern Spain).Viruses. 2019 Jul 5;11(7):618. doi: 10.3390/v11070618. Viruses. 2019. PMID: 31284466 Free PMC article.
-
Hepatitis E virus genotype 3 in mussels (Mytilus galloprovinciallis), Spain.Food Microbiol. 2016 Sep;58:13-5. doi: 10.1016/j.fm.2016.03.009. Epub 2016 Mar 15. Food Microbiol. 2016. PMID: 27217353
-
First Report of the Presence of Hepatitis E Virus in Scottish-Harvested Shellfish Purchased at Retail Level.Food Environ Virol. 2018 Jun;10(2):217-221. doi: 10.1007/s12560-018-9337-5. Epub 2018 Feb 13. Food Environ Virol. 2018. PMID: 29442296 Free PMC article.
-
Light and Darkness: Prevalence of Hepatitis E Virus Infection among the General Population.Scientifica (Cairo). 2014;2014:481016. doi: 10.1155/2014/481016. Epub 2014 Feb 10. Scientifica (Cairo). 2014. PMID: 24672733 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Occurrence of Human Enteric Viruses in Water Sources and Shellfish: A Focus on Africa.Food Environ Virol. 2021 Mar;13(1):1-31. doi: 10.1007/s12560-020-09456-8. Epub 2021 Jan 27. Food Environ Virol. 2021. PMID: 33501612 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hepatitis E Virus in the Role of an Emerging Food-Borne Pathogen.Microorganisms. 2025 Apr 12;13(4):885. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms13040885. Microorganisms. 2025. PMID: 40284721 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Seroprevalence of hepatitis E in adults in Brazil: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Infect Dis Poverty. 2019 Jan 16;8(1):3. doi: 10.1186/s40249-018-0514-4. Infect Dis Poverty. 2019. PMID: 30646964 Free PMC article.
-
Zoonotic Hepatitis E Virus: Classification, Animal Reservoirs and Transmission Routes.Viruses. 2016 Oct 3;8(10):270. doi: 10.3390/v8100270. Viruses. 2016. PMID: 27706110 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Epidemiological investigation of a tap water-mediated hepatitis E virus genotype 4 outbreak in Zhejiang Province, China.Epidemiol Infect. 2016 Dec;144(16):3387-3399. doi: 10.1017/S0950268816001898. Epub 2016 Aug 22. Epidemiol Infect. 2016. PMID: 27546066 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Fu H., Li L., Zhu Y., Wang L., Geng J., Chang Y., Xue C., Du G., Li Y., Zhuang H. Hepatitis E virus infection among animals and humans in Xinjiang, China: Possibility of swine to human transmission of sporadic hepatitis E in an endemic area. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2010;82:961–966. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.2010.09-0689. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

