Application of QUAL2K model to assess ecological purification technology for a polluted river
- PMID: 25689997
- PMCID: PMC4344721
- DOI: 10.3390/ijerph120202215
Application of QUAL2K model to assess ecological purification technology for a polluted river
Abstract
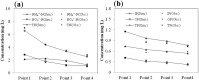
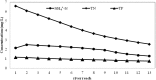
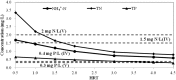
Industrialization and urbanization have caused water pollution and ecosystem degradation, especially in urban canals and rivers in China; accordingly, effective water quality improvement programs are needed. In this study, the Tianlai River in Jiangsu, China was taken as a research site, and a combination of ecological purification technologies consisting of biological rope, phytoremediation, and activated carbon were applied in a laboratory-scale study to examine degradation coefficients under dynamic water conditions. Coefficients were then input into the QUAL2K model to simulate various hypothetical scenarios and determine the minimum density of ecological purification combination and hydraulic retention time (HRT) to meet Grade V or IV of the China standard for surface water. The minimum densities for Grade V and IV were 1.6 times and 2 times the experimental density, while the minimum HRTs for Grade V and IV were 2.4 day and 3 day. The results of this study should provide a practical and efficient design method for ecological purification programs.
Figures




References
-
- Nahlik A.M., Mitsch W.J. Tropical treatment wetlands dominated by free-floating macrophytes for water quality improvement in Costa Rica. Ecol. Eng. 2006;28:246–257. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoleng.2006.07.006. - DOI
-
- Wang G.X., Zhang L.M., Chua H., Li X.D. A mosaic community of macrophytes for the ecological remediation of eutrophic shallow lakes. Ecol. Eng. 2009;35:582–590. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoleng.2008.06.006. - DOI
-
- Donnert D., Salecker M. Elimination of phosphorus from municipal and industrial waste water. Water Sci. Technol. 1999;40:195–202. doi: 10.1016/S0273-1223(99)00501-6. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

