Proteomic-based approach to gain insight into reprogramming of THP-1 cells exposed to Leishmania donovani over an early temporal window
- PMID: 25690103
- PMCID: PMC4399049
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.02833-14
Proteomic-based approach to gain insight into reprogramming of THP-1 cells exposed to Leishmania donovani over an early temporal window
Abstract
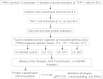
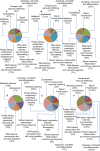
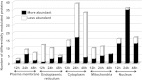
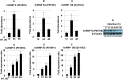
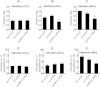
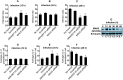
Leishmania donovani, a protozoan parasite, is the causative agent of visceral leishmaniasis. It lives and multiplies within the harsh environment of macrophages. In order to investigate how intracellular parasite manipulate the host cell environment, we undertook a quantitative proteomic study of human monocyte-derived macrophages (THP-1) following infection with L. donovani. We used the isobaric tags for relative and absolute quantification (iTRAQ) method and liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS) to compare expression profiles of noninfected and L. donovani-infected THP-1 cells. We detected modifications of protein expression in key metabolic pathways, including glycolysis and fatty acid oxidation, suggesting a global reprogramming of cell metabolism by the parasite. An increased abundance of proteins involved in gene transcription, RNA splicing (heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoproteins [hnRNPs]), histones, and DNA repair and replication was observed at 24 h postinfection. Proteins involved in cell survival and signal transduction were more abundant at 24 h postinfection. Several of the differentially expressed proteins had not been previously implicated in response to the parasite, while the others support the previously identified proteins. Selected proteomics results were validated by real-time PCR and immunoblot analyses. Similar changes were observed in L. donovani-infected human monocyte-derived primary macrophages. The effect of RNA interference (RNAi)-mediated gene knockdown of proteins validated the relevance of the host quantitative proteomic screen. Our findings indicate that the host cell proteome is modulated after L. donovani infection, provide evidence for global reprogramming of cell metabolism, and demonstrate the complex relations between the host and parasite at the molecular level.
Copyright © 2015, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved.
Figures



References
-
- Herwaldt BL. 1999. Leishmaniasis. Lancet 354:1191–1199. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

