Ischemic optic neuropathies and their models: disease comparisons, model strengths and weaknesses
- PMID: 25690987
- PMCID: PMC4556370
- DOI: 10.1007/s10384-015-0373-5
Ischemic optic neuropathies and their models: disease comparisons, model strengths and weaknesses
Abstract
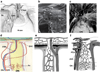
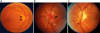
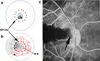
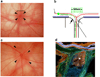
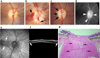
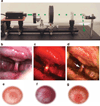
Ischemic optic neuropathies (IONs) describe a group of diseases that specifically target the optic nerve and result in sudden vision loss. These include nonarteritic and arteritic anterior ischemic optic neuropathy (NAION and AAION) and posterior ischemic optic neuropathy (NPION, APION). Until recently, little was known of the mechanisms involved in ION damage, due to a lack of information about the mechanisms associated with these diseases. This review discusses the new models that closely mimic these diseases (rodent NAION, primate NAION, rodent PION). These models have enabled closer dissection of the mechanisms involved with the pathophysiology of these disorders and enable identification of relevant mechanisms and potential pathways for effective therapeutic intervention. Descriptions of the different models are included, and comparisons between the models, their relative similarities with the clinical disease, as well as differences are discussed.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Arnold AC. Ischemic optic neuropathies. Ophthalmol Clin North Am. 2001;14:83–98. - PubMed
-
- Hayreh SS. Posterior ischaemic optic neuropathy: clinical features, pathogenesis, and management. Eye (Lond) 1969;18:1188–1206. - PubMed
-
- Anderson DR. Ultrastructure of human and monkey lamina cribrosa and optic nerve head. Arch Ophthalmol. 1969;82:800–814. - PubMed
-
- Cioffi GA, Van Buskirk EM. Microvasculature of the anterior optic nerve. Surv Ophthalmol. 1994;38(Suppl):S107. - PubMed
-
- Morrison JC, Johnson EC, Cepurna WO, Funk RH. Microvasculature of the rat optic nerve head. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1999;1999(40):1702–1709. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

