Epigenomic footprints across 111 reference epigenomes reveal tissue-specific epigenetic regulation of lincRNAs
- PMID: 25691256
- PMCID: PMC4335353
- DOI: 10.1038/ncomms7370
Epigenomic footprints across 111 reference epigenomes reveal tissue-specific epigenetic regulation of lincRNAs
Abstract
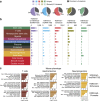
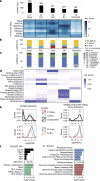
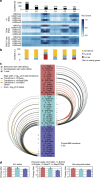
Tissue-specific expression of lincRNAs suggests developmental and cell-type-specific functions, yet tissue specificity was established for only a small fraction of lincRNAs. Here, by analysing 111 reference epigenomes from the NIH Roadmap Epigenomics project, we determine tissue-specific epigenetic regulation for 3,753 (69% examined) lincRNAs, with 54% active in one of the 14 cell/tissue clusters and an additional 15% in two or three clusters. A larger fraction of lincRNA TSSs is marked in a tissue-specific manner by H3K4me1 than by H3K4me3. The tissue-specific lincRNAs are strongly linked to tissue-specific pathways and undergo distinct chromatin state transitions during cellular differentiation. Polycomb-regulated lincRNAs reside in the bivalent state in embryonic stem cells and many of them undergo H3K27me3-mediated silencing at early stages of differentiation. The exquisitely tissue-specific epigenetic regulation of lincRNAs and the assignment of a majority of them to specific tissue types will inform future studies of this newly discovered class of genes.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

