Eravacycline (TP-434) is efficacious in animal models of infection
- PMID: 25691636
- PMCID: PMC4394802
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.04354-14
Eravacycline (TP-434) is efficacious in animal models of infection
Abstract
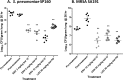
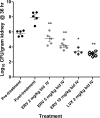
Eravacycline is a novel broad-spectrum fluorocycline antibiotic being developed for a wide range of serious infections. Eravacycline was efficacious in mouse septicemia models, demonstrating 50% protective dose (PD50) values of ≤ 1 mg/kg of body weight once a day (q.d.) against Staphylococcus aureus, including tetracycline-resistant isolates of methicillin-resistant S. aureus (MRSA), and Streptococcus pyogenes. The PD50 values against Escherichia coli isolates were 1.2 to 4.4 mg/kg q.d. In neutropenic mouse thigh infection models with methicillin-sensitive S. aureus (MSSA) and S. pyogenes, eravacycline produced 2 log10 reductions in CFU at single intravenous (i.v.) doses ranging from 0.2 to 9.5 mg/kg. In a neutropenic mouse lung infection model, eravacycline administered i.v. at 10 mg/kg twice a day (b.i.d.) reduced the level of tetracycline-resistant MRSA in the lung equivalent to that of linezolid given orally (p.o.) at 30 mg/kg b.i.d. At i.v. doses of 3 to 12 mg/kg b.i.d., eravacycline was more efficacious against tetracycline-resistant Streptococcus pneumoniae in a neutropenic lung infection model than linezolid p.o. at 30 mg/kg b.i.d. Eravacycline showed good efficacy at 2 to 10 mg/kg i.v. b.i.d., producing up to a 4.6 log10 CFU reduction in kidney bacterial burden in a model challenged with a uropathogenic E. coli isolate. Eravacycline was active in multiple murine models of infection against clinically important Gram-positive and Gram-negative pathogens.
Copyright © 2015, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Pharmacodynamics of a new cephalosporin, PPI-0903 (TAK-599), active against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in murine thigh and lung infection models: identification of an in vivo pharmacokinetic-pharmacodynamic target.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2006 Apr;50(4):1376-83. doi: 10.1128/AAC.50.4.1376-1383.2006. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2006. PMID: 16569855 Free PMC article.
-
In Vivo Pharmacodynamic Target Investigation of Two Bacterial Topoisomerase Inhibitors, ACT-387042 and ACT-292706, in the Neutropenic Murine Thigh Model against Streptococcus pneumoniae and Staphylococcus aureus.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2016 May 23;60(6):3626-32. doi: 10.1128/AAC.00363-16. Print 2016 Jun. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2016. PMID: 27044547 Free PMC article.
-
Antibacterial Efficacy of Eravacycline In Vivo against Gram-Positive and Gram-Negative Organisms.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2016 Jul 22;60(8):5001-5. doi: 10.1128/AAC.00366-16. Print 2016 Aug. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2016. PMID: 27353265 Free PMC article.
-
Review of Eravacycline, a Novel Fluorocycline Antibacterial Agent.Drugs. 2016 Apr;76(5):567-88. doi: 10.1007/s40265-016-0545-8. Drugs. 2016. PMID: 26863149 Review.
-
Eravacycline, a newly approved fluorocycline.Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2019 Oct;38(10):1787-1794. doi: 10.1007/s10096-019-03590-3. Epub 2019 Jun 7. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2019. PMID: 31175478 Review.
Cited by
-
Pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic evaluation of the atypical tetracyclines chelocardin and amidochelocardin in murine infection models.Microbiol Spectr. 2024 Jan 11;12(1):e0128923. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.01289-23. Epub 2023 Dec 4. Microbiol Spectr. 2024. PMID: 38047701 Free PMC article.
-
Heterocyclyl tetracyclines. 2. 7-Methoxy-8-pyrrolidinyltetracyclines: discovery of TP-2758, a potent, orally efficacious antimicrobial against Gram-negative pathogens.J Antibiot (Tokyo). 2018 Feb;71(2):287-297. doi: 10.1038/ja.2017.86. Epub 2017 Jul 26. J Antibiot (Tokyo). 2018. PMID: 28743974
-
In Vivo Assessment of Phage and Linezolid Based Implant Coatings for Treatment of Methicillin Resistant S. aureus (MRSA) Mediated Orthopaedic Device Related Infections.PLoS One. 2016 Jun 22;11(6):e0157626. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0157626. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27333300 Free PMC article.
-
In vitro susceptibility of β-lactamase-producing carbapenem-resistant Enterobacteriaceae (CRE) to eravacycline.J Antibiot (Tokyo). 2016 Aug;69(8):600-4. doi: 10.1038/ja.2016.73. Epub 2016 Jun 29. J Antibiot (Tokyo). 2016. PMID: 27353166
-
Re-establishing the utility of tetracycline-class antibiotics for current challenges with antibiotic resistance.Ann Med. 2022 Dec;54(1):1686-1700. doi: 10.1080/07853890.2022.2085881. Ann Med. 2022. PMID: 35723082 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. 2013. Antibiotic resistance threats in the United States, 2013. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, Atlanta, GA.
-
- Roberts RR, Hota B, Ahmad I, Scott RD II, Foster SD, Abbasi F, Schabowski S, Kampe LM, Ciavarella GG, Supino M, Naples J, Cordell R, Levy SB, Weinstein RA. 2009. Hospital and societal costs of antimicrobial-resistant infections in a Chicago teaching hospital: implications for antibiotic stewardship. Clin Infect Dis 49:1175–1184. doi:10.1086/605630. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

