HDAC inhibition prevents white matter injury by modulating microglia/macrophage polarization through the GSK3β/PTEN/Akt axis
- PMID: 25691750
- PMCID: PMC4352818
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1501441112
HDAC inhibition prevents white matter injury by modulating microglia/macrophage polarization through the GSK3β/PTEN/Akt axis
Abstract
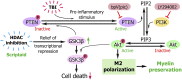
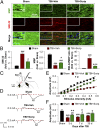
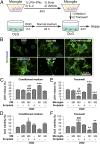
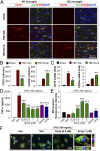
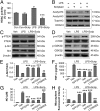
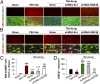
Severe traumatic brain injury (TBI) elicits destruction of both gray and white matter, which is exacerbated by secondary proinflammatory responses. Although white matter injury (WMI) is strongly correlated with poor neurological status, the maintenance of white matter integrity is poorly understood, and no current therapies protect both gray and white matter. One candidate approach that may fulfill this role is inhibition of class I/II histone deacetylases (HDACs). Here we demonstrate that the HDAC inhibitor Scriptaid protects white matter up to 35 d after TBI, as shown by reductions in abnormally dephosphorylated neurofilament protein, increases in myelin basic protein, anatomic preservation of myelinated axons, and improved nerve conduction. Furthermore, Scriptaid shifted microglia/macrophage polarization toward the protective M2 phenotype and mitigated inflammation. In primary cocultures of microglia and oligodendrocytes, Scriptaid increased expression of microglial glycogen synthase kinase 3 beta (GSK3β), which phosphorylated and inactivated phosphatase and tensin homologue (PTEN), thereby enhancing phosphatidylinositide 3-kinases (PI3K)/Akt signaling and polarizing microglia toward M2. The increase in GSK3β in microglia and their phenotypic switch to M2 was associated with increased preservation of neighboring oligodendrocytes. These findings are consistent with recent findings that microglial phenotypic switching modulates white matter repair and axonal remyelination and highlight a previously unexplored role for HDAC activity in this process. Furthermore, the functions of GSK3β may be more subtle than previously thought, in that GSK3β can modulate microglial functions via the PTEN/PI3K/Akt signaling pathway and preserve white matter homeostasis. Thus, inhibition of HDACs in microglia is a potential future therapy in TBI and other neurological conditions with white matter destruction.
Keywords: inflammation; microglial polarization; myelination; oligodendrocyte; traumatic brain injury.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
HDAC inhibition reduces white matter injury after intracerebral hemorrhage.J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2021 May;41(5):958-974. doi: 10.1177/0271678X20942613. Epub 2020 Jul 23. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2021. PMID: 32703113 Free PMC article.
-
Selective activation of cannabinoid receptor-2 reduces white matter injury via PERK signaling in a rat model of traumatic brain injury.Exp Neurol. 2022 Jan;347:113899. doi: 10.1016/j.expneurol.2021.113899. Epub 2021 Oct 20. Exp Neurol. 2022. PMID: 34678230
-
Tetrahydrocurcumin Protects Against GSK3β/PTEN/PI3K/Akt-Mediated Neuroinflammatory Responses and Microglial Polarization Following Traumatic Brain Injury.Mol Neurobiol. 2024 Sep;61(9):7026-7036. doi: 10.1007/s12035-024-04034-6. Epub 2024 Feb 17. Mol Neurobiol. 2024. PMID: 38368289
-
Myelin and oligodendrocyte lineage cells in white matter pathology and plasticity after traumatic brain injury.Neuropharmacology. 2016 Nov;110(Pt B):654-659. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2015.04.029. Epub 2015 May 9. Neuropharmacology. 2016. PMID: 25963414 Review.
-
White matter involvement after TBI: Clues to axon and myelin repair capacity.Exp Neurol. 2016 Jan;275 Pt 3:328-333. doi: 10.1016/j.expneurol.2015.02.011. Epub 2015 Feb 16. Exp Neurol. 2016. PMID: 25697845 Review.
Cited by
-
Severity-Dependent Long-Term Spatial Learning-Memory Impairment in a Mouse Model of Traumatic Brain Injury.Transl Stroke Res. 2016 Dec;7(6):512-520. doi: 10.1007/s12975-016-0483-5. Epub 2016 Aug 18. Transl Stroke Res. 2016. PMID: 27539574
-
Depletion of muscularis macrophages ameliorates inflammation-driven dysmotility in murine colitis model.Sci Rep. 2023 Dec 17;13(1):22451. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-50059-7. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 38105266 Free PMC article.
-
Cornel Iridoid Glycoside Protects Against White Matter Lesions Induced by Cerebral Ischemia in Rats via Activation of the Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor/Neuregulin-1 Pathway.Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat. 2019 Dec 2;15:3327-3340. doi: 10.2147/NDT.S228417. eCollection 2019. Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat. 2019. PMID: 31819458 Free PMC article.
-
Systemic hypoxia led to little retinal neuronal loss and dramatic optic nerve glial response.Exp Eye Res. 2020 Apr;193:107957. doi: 10.1016/j.exer.2020.107957. Epub 2020 Feb 4. Exp Eye Res. 2020. PMID: 32032627 Free PMC article.
-
Xinnao Shutong Modulates the Neuronal Plasticity Through Regulation of Microglia/Macrophage Polarization Following Chronic Cerebral Hypoperfusion in Rats.Front Physiol. 2018 May 15;9:529. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2018.00529. eCollection 2018. Front Physiol. 2018. PMID: 29867570 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Rosenfeld JV, et al. Early management of severe traumatic brain injury. Lancet. 2012;380(9847):1088–1098. - PubMed
-
- Spitz G, Maller JJ, O’Sullivan R, Ponsford JL. White matter integrity following traumatic brain injury: The association with severity of injury and cognitive functioning. Brain Topogr. 2013;26(4):648–660. - PubMed
-
- Betz J, Zhuo J, Roy A, Shanmuganathan K, Gullapalli RP. Prognostic value of diffusion tensor imaging parameters in severe traumatic brain injury. J Neurotrauma. 2012;29(7):1292–1305. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

