Biology of renal tumour cancer stem cells applied in medicine
- PMID: 25691821
- PMCID: PMC4322535
- DOI: 10.5114/wo.2014.47128
Biology of renal tumour cancer stem cells applied in medicine
Abstract
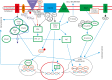
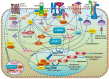
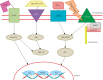
The present article highlights the diverse role of stem cells in normal kidney and renal cancer, with special emphasis on surface markers. Proteins such as CD105 and CD133 have been reported as being significant in clear cell renal cell carcinoma (ccRCC) cancer stem cells. The role of normal kidney progenitor cells and their surface markers is compared with the role of those surface markers in ccRCC. Subsequently, we state the current hypothesis about origin of tumour-initiating cells along with their clinical and prognostic potential in RCC. Finally, we present future perspectives with respect to recent studies.
Keywords: cancer stem cells; renal cancer; tumour-initiating cells.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Comparative Gene Expression Profiling of Primary and Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma Stem Cell-Like Cancer Cells.PLoS One. 2016 Nov 3;11(11):e0165718. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0165718. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27812180 Free PMC article.
-
Functional significance of CD105-positive cells in papillary renal cell carcinoma.BMC Cancer. 2017 Jan 5;17(1):21. doi: 10.1186/s12885-016-2985-7. BMC Cancer. 2017. PMID: 28056882 Free PMC article.
-
Gene expression analysis in clear cell renal cell carcinoma using gene set enrichment analysis for biostatistical management.BJU Int. 2011 Jul;108(2 Pt 2):E29-35. doi: 10.1111/j.1464-410X.2010.09794.x. Epub 2011 Mar 16. BJU Int. 2011. PMID: 21435154
-
Diagnostic and prognostic tissuemarkers in clear cell and papillary renal cell carcinoma.Cancer Biomark. 2010;7(6):261-8. doi: 10.3233/CBM-2010-0195. Cancer Biomark. 2010. PMID: 21694464 Review.
-
The Role of Hypoxia and Cancer Stem Cells in Renal Cell Carcinoma Pathogenesis.Stem Cell Rev Rep. 2015 Dec;11(6):919-43. doi: 10.1007/s12015-015-9611-y. Stem Cell Rev Rep. 2015. PMID: 26210994 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Renal Cancer Stem Cells: Characterization and Targeted Therapies.Stem Cells Int. 2016;2016:8342625. doi: 10.1155/2016/8342625. Epub 2016 May 15. Stem Cells Int. 2016. PMID: 27293448 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Reduced expression of CXCR4, a novel renal cancer stem cell marker, is associated with high-grade renal cell carcinoma.J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2017 Jan;143(1):95-104. doi: 10.1007/s00432-016-2239-8. Epub 2016 Sep 16. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2017. PMID: 27638770 Free PMC article.
-
Ecto-5'-nucleotidase (CD73) is a biomarker for clear cell renal carcinoma stem-like cells.Oncotarget. 2017 May 9;8(19):31977-31992. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.16667. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 28404888 Free PMC article.
-
Co-expression of Cancer Stem Cell Markers OCT4 and NANOG Predicts Poor Prognosis in Renal Cell Carcinomas.Sci Rep. 2018 Aug 6;8(1):11739. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-30168-4. Sci Rep. 2018. PMID: 30082842 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of endogenous hydrogen sulfide production in clear-cell renal cell carcinoma cell lines and xenografts restricts their growth, survival and angiogenic potential.Nitric Oxide. 2015 Sep 15;49:26-39. doi: 10.1016/j.niox.2015.06.001. Epub 2015 Jun 9. Nitric Oxide. 2015. PMID: 26068241 Free PMC article.
References
-
- NCI. Definition of renal cell cancer; http://www.cancer.gov/dictionary?cdrid=44988.
-
- Buczek M, Escudier B, Bartnik E, Szczylik C, Czarnecka A. Resistance to tyrosine kinase inhibitors in clear cell renal cell carcinoma: from the patient's bed to molecular mechanisms. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2014;1845:31–41. - PubMed
-
- Mattei J, da Silva RD, Sehrt D, Molina WR, Kim FJ. Targeted therapy in metastatic renal carcinoma. Cancer Lett. 2014;343:156–60. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
