Circulating ghrelin levels and obestatin/ghrelin ratio as a marker of activity in ulcerative colitis
- PMID: 25691845
- PMCID: PMC4316225
- DOI: 10.5217/ir.2015.13.1.68
Circulating ghrelin levels and obestatin/ghrelin ratio as a marker of activity in ulcerative colitis
Abstract
Background/aims: Ghrelin levels are known to increase in patients with ulcerative colitis (UC), but serum obestatin levels in UC patients are not well elucidated. The aim of this study was to examine the relationship between serum ghrelin and obestatin levels and disease activity in UC patients.
Methods: The serum ghrelin and obestatin levels were measured in 21 UC patients (12 with active disease and 9 in remission) using enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. The relationship between the circulating levels of these 2 hormones and disease activity was analyzed. The colonic mucosal mRNA expression of ghrelin and obestatin was measured by quantitative reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction.
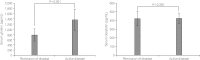
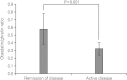
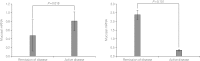
Results: The mean serum ghrelin values were significantly higher in patients with active disease than in patients with remission (1370.6±404.3 vs. 783.5±235.3 pg/mL, P=0.001). Colonic mucosal mRNA expression of ghrelin was also significantly higher in patients with active disease than in patients in remission (0.805±0.214 vs. 0.481±0.356, P=0.018). However, the mean serum obestatin levels and colonic mucosal mRNA expression of obestatin were not significantly different between both groups. The circulating obestatin/ghrelin ratio was significantly lower in patients with active UC than in patients in remission (0.32±0.08 vs. 0.58±0.20, P=0.001).
Conclusions: The serum ghrelin levels and the obestatin/ghrelin ratio were related to the activity of UC, but serum obestatin was not related to activity of UC. The ghrelin levels and the obestatin/ghrelin ratio could serve as activity markers in patients with UC.
Keywords: Colitis, ulcerative; Disease activity; Ghrelin; Obestatin; Ratio.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest: None.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Obestatin/ghrelin ratio: a new activity index in inflammatory bowel diseases.Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2009 Oct;15(10):1557-61. doi: 10.1002/ibd.20940. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2009. PMID: 19408254
-
Unveiling the Ghrelin and Obestatin Roles in Inflammatory Bowel Diseases: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis Assessing Their Pathogenic Implications and Biomarker Utility.Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2024 Apr 3;30(4):629-640. doi: 10.1093/ibd/izad202. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2024. PMID: 37669127
-
Circulating levels of leptin, adiponectin, resistin, and ghrelin in inflammatory bowel disease.Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2006 Feb;12(2):100-5. doi: 10.1097/01.MIB.0000200345.38837.46. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2006. PMID: 16432373
-
Ghrelin to obestatin ratio in maternal serum in pregnancies complicated by intrauterine growth restriction.Clin Exp Obstet Gynecol. 2017;44(3):364-369. Clin Exp Obstet Gynecol. 2017. PMID: 29949274
-
Ghrelin and obestatin levels in rheumatoid arthritis.Inflammation. 2008 Oct;31(5):329-35. doi: 10.1007/s10753-008-9082-2. Inflammation. 2008. PMID: 18677577
Cited by
-
L-Glutamine and Physical Exercise Prevent Intestinal Inflammation and Oxidative Stress Without Improving Gastric Dysmotility in Rats with Ulcerative Colitis.Inflammation. 2021 Apr;44(2):617-632. doi: 10.1007/s10753-020-01361-3. Epub 2020 Oct 31. Inflammation. 2021. PMID: 33128666
-
Treatment with Obestatin-A Ghrelin Gene-Encoded Peptide-Reduces the Severity of Experimental Colitis Evoked by Trinitrobenzene Sulfonic Acid.Int J Mol Sci. 2018 Jun 1;19(6):1643. doi: 10.3390/ijms19061643. Int J Mol Sci. 2018. PMID: 29865176 Free PMC article.
-
Plasma ghrelin and leptin in patients with inflammatory bowel disease and its association with nutritional status.Saudi J Gastroenterol. 2017 May-Jun;23(3):199-205. doi: 10.4103/sjg.SJG_575_16. Saudi J Gastroenterol. 2017. PMID: 28611344 Free PMC article.
-
TNF-α inhibits SCF, ghrelin, and substance P expressions through the NF-κB pathway activation in interstitial cells of Cajal.Braz J Med Biol Res. 2018;51(6):e7065. doi: 10.1590/1414-431x20187065. Epub 2018 Apr 23. Braz J Med Biol Res. 2018. PMID: 29694505 Free PMC article.
-
Correlation between the tissue ghrelin presence, disease activity and laboratory parameters in ulcerative colitis patients; immunohistochemical study.PLoS One. 2022 Nov 9;17(11):e0276065. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0276065. eCollection 2022. PLoS One. 2022. PMID: 36350879 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Goh J, O'Morain CA. Review article: nutrition and adult inflammatory bowel disease. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2003;17:307–320. - PubMed
-
- Bamias G, Nyce MR, De La, Cominelli F. New concepts in the pathophysiology of inflammatory bowel disease. Ann Intern Med. 2005;143:895–904. - PubMed
-
- Karmiris K, Koutroubakis IE, Xidakis C, Polychronaki M, Voudouri T, Kouroumalis EA. Circulating levels of leptin, adiponectin, resistin, and ghrelin in inflammatory bowel disease. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2006;12:100–105. - PubMed
-
- Deboer MD. Use of ghrelin as a treatment for inflammatory bowel disease: mechanistic considerations. Int J Pept. doi: 10.1155/2011/189242. Published online 9 August 2011. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- DeBoer MD. Emergence of ghrelin as a treatment for cachexia syndromes. Nutrition. 2008;24:806–814. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources