Photopolarization of Fucus zygotes is determined by time sensitive vectorial addition of environmental cues during axis amplification
- PMID: 25691888
- PMCID: PMC4315017
- DOI: 10.3389/fpls.2015.00026
Photopolarization of Fucus zygotes is determined by time sensitive vectorial addition of environmental cues during axis amplification
Abstract
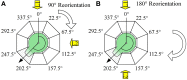
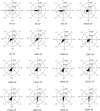
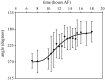
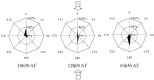
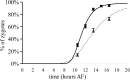
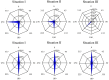
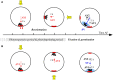
Fucoid zygotes have been extensively used to study cell polarization and asymmetrical cell division. Fertilized eggs are responsive to different environmental cues (e.g., light, gravity) for a long period before the polarity is fixed and the cells germinate accordingly. First, it is commonly believed that the direction and sense of the polarization vector are established simultaneously as indicated by the formation of an F-actin patch. Secondly, upon reorientation of the zygote, a new polar gradient is formed and it is assumed that the position of the future rhizoid pole is only influenced by the latter. Here we tested these two hypotheses investigating photopolarization in Fucus zygotes by reorienting zygotes 90° relative to a unilateral light source at different time points during the first cell cycle. We conclude that fixation of direction and sense of the polarization vector is indeed established simultaneously. However, the experiments yielded a distribution of polarization axes that cannot be explained if only the last environmental cue is supposed to determine the polarization axis. We conclude that our observations, together with published findings, can only be explained by assuming imprinting of the different polarization vectors and their integration as a vectorial sum at the moment of axis fixation. This way cells will average different serially perceived cues resulting in a polarization vector representative of the dynamic intertidal environment, instead of betting exclusively on the perceived vector at the moment of axis fixation.
Keywords: Brown algae; Fucus; asymmetrical cell division; embryogenesis; intrinsic factors; patterning; polarization; positional information.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Ca2+ and Calmodulin Dynamics during Photopolarization in Fucus serratus Zygotes.Plant Physiol. 1997 Sep;115(1):249-261. doi: 10.1104/pp.115.1.249. Plant Physiol. 1997. PMID: 12223805 Free PMC article.
-
Establishment and expression of cellular polarity in fucoid zygotes.Microbiol Rev. 1992 Jun;56(2):316-39. doi: 10.1128/mr.56.2.316-339.1992. Microbiol Rev. 1992. PMID: 1620068 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Roles of secretion and the cytoskeleton in cell adhesion and polarity establishment in Pelvetia compressa zygotes.Dev Biol. 1998 Jun 1;198(1):45-56. Dev Biol. 1998. PMID: 9640331
-
Isolation of Fucus serratus Gametes and Cultivation of the Zygotes.Bio Protoc. 2017 Jul 20;7(14):e2408. doi: 10.21769/BioProtoc.2408. eCollection 2017 Jul 20. Bio Protoc. 2017. PMID: 34541138 Free PMC article.
-
Symmetry breaking in the zygotes of the fucoid algae: controversies and recent progress.Curr Top Dev Biol. 1999;44:101-25. doi: 10.1016/s0070-2153(08)60468-8. Curr Top Dev Biol. 1999. PMID: 9891878 Review.
Cited by
-
Cell-Autonomous and Non-Cell-Autonomous Mechanisms Concomitantly Regulate the Early Developmental Pattern in the Kelp Saccharina latissima Embryo.Plants (Basel). 2024 May 13;13(10):1341. doi: 10.3390/plants13101341. Plants (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38794413 Free PMC article.
-
MUM, a maternal unknown message, inhibits early establishment of the medio-lateral axis in the embryo of the kelp Saccharina latissima.Development. 2024 Oct 15;151(20):dev202732. doi: 10.1242/dev.202732. Epub 2024 Sep 13. Development. 2024. PMID: 39190296 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alessa L., Kropf D. L. (1999). F-actin marks the rhizoid pole in living Pelvetia compressa zygotes. Development 126, 201–209. - PubMed
-
- Batschelet E. (1972). Recent statistical methods for orientation data, in Animal Orientation and Navigation, eds Galler S. R., Schmidt-Koenig K., Jacobs G. J., Belleview R. E. (Washington D.C.: NASA; ), 61.
-
- Batschelet E. (1978). Second-order statistical analysis of directions, in Animal migration, Navigation, and Homing, eds Schmidt-Koenig K., Keeton W. T. (Berlin: Springer-Verlag; ), 1–24.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

