Nonlinear Bayesian estimation of BOLD signal under non-Gaussian noise
- PMID: 25691911
- PMCID: PMC4321086
- DOI: 10.1155/2015/389875
Nonlinear Bayesian estimation of BOLD signal under non-Gaussian noise
Abstract
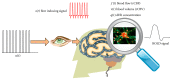
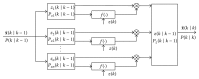
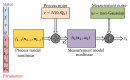
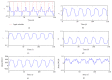
Modeling the blood oxygenation level dependent (BOLD) signal has been a subject of study for over a decade in the neuroimaging community. Inspired from fluid dynamics, the hemodynamic model provides a plausible yet convincing interpretation of the BOLD signal by amalgamating effects of dynamic physiological changes in blood oxygenation, cerebral blood flow and volume. The nonautonomous, nonlinear set of differential equations of the hemodynamic model constitutes the process model while the weighted nonlinear sum of the physiological variables forms the measurement model. Plagued by various noise sources, the time series fMRI measurement data is mostly assumed to be affected by additive Gaussian noise. Though more feasible, the assumption may cause the designed filter to perform poorly if made to work under non-Gaussian environment. In this paper, we present a data assimilation scheme that assumes additive non-Gaussian noise, namely, the e-mixture noise, affecting the measurements. The proposed filter MAGSF and the celebrated EKF are put to test by performing joint optimal Bayesian filtering to estimate both the states and parameters governing the hemodynamic model under non-Gaussian environment. Analyses using both the synthetic and real data reveal superior performance of the MAGSF as compared to EKF.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A state-space model of the hemodynamic approach: nonlinear filtering of BOLD signals.Neuroimage. 2004 Feb;21(2):547-67. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2003.09.052. Neuroimage. 2004. PMID: 14980557
-
Bayesian model comparison in nonlinear BOLD fMRI hemodynamics.Neural Comput. 2008 Mar;20(3):738-55. doi: 10.1162/neco.2007.07-06-282. Neural Comput. 2008. PMID: 18045013
-
Modeling of nonlinear biological phenomena modeled by S-systems.Math Biosci. 2014 Mar;249:75-91. doi: 10.1016/j.mbs.2014.01.011. Epub 2014 Feb 11. Math Biosci. 2014. PMID: 24524881
-
Modeling the hemodynamic response to brain activation.Neuroimage. 2004;23 Suppl 1:S220-33. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2004.07.013. Neuroimage. 2004. PMID: 15501093 Review.
-
Parametric Bayesian filters for nonlinear stochastic dynamical systems: a survey.IEEE Trans Cybern. 2013 Dec;43(6):1607-24. doi: 10.1109/TSMCC.2012.2230254. IEEE Trans Cybern. 2013. PMID: 23757593 Review.
Cited by
-
A Nonlinear Framework of Delayed Particle Smoothing Method for Vehicle Localization under Non-Gaussian Environment.Sensors (Basel). 2016 May 13;16(5):692. doi: 10.3390/s16050692. Sensors (Basel). 2016. PMID: 27187405 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Friston K. J., Holmes A. P., Worsley K. J., Poline J.-P., Frith C. D., Frackowiak R. S. J. Statistical parametric maps in functional imaging: a general linear approach. Human Brain Mapping. 1994;2(4):189–210. doi: 10.1002/hbm.460020402. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

