Comparison of human adipose-derived stem cells and chondroitinase ABC transplantation on locomotor recovery in the contusion model of spinal cord injury in rats
- PMID: 25691946
- PMCID: PMC4322153
Comparison of human adipose-derived stem cells and chondroitinase ABC transplantation on locomotor recovery in the contusion model of spinal cord injury in rats
Abstract
Objectives: Spinal cord injury (SCI) is one of the most serious clinical diseases and its treatment has been a subject of interest to researchers. There are two important therapeutic strategies in the treatment of SCI: replacing lost tissue cells through cells implantation and scar elimination. Therefore, in this study we used human adipose-derived stem cells (hADSCs) implantation and injection of Chondroitinase ABC. Aim of present study was to answer to this question: which one is more efficient for Improvement of locomotor recovery after SCI in rat? Transplantation of hADSCs or injection of ChABC.
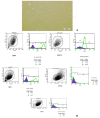
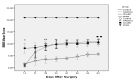
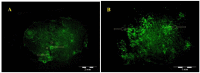
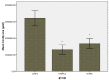
Materials and methods: The spinal cord of rats was injured by contusion using a weight-drop at the level of T8-9, the hADSCs and Chondroitinase ABC were infused in to the spinal cord tissue after injury. BBB test was performed and recorded for each animal weekly for 8 weeks. After the 8(th) weeks, Serial cross-sections were stained with cresyl violet and examined under a light microscope and area of cavity in the spinal cord was measured.
Results: At 8(th) weeks after injection, hADSCs and ChABC significantly promote locomotor function (P<0.01) and spinal cords of hADSCs and ChABC group had cavities much smaller than those of the control group (P<0.001).
Conclusion: Results of the present study shows dealing with inappropriate neuro-inhibitory environment and glial scar by ChABC have equal role compare to cell therapy (with hADSCs) for improving motor function after SCI and this result in adoption of proper therapeutic strategies for SCI intervention is important.
Keywords: BBB; Chondroitinase ABC; Contusion; Spinal Cord Injury; hADSCs.
Figures


References
-
- Pearse DD, Sanchez AR, Pereira FC, Andrade CM, Puzis R, Pressman Y, et al. Transplantation of Schwann cells and/or olfactory ensheathing glia into the contused spinal cord: Survival migration axon association nd functional recovery. Glia . 2007;55:976–1000. - PubMed
-
- Hulsebosch CE. Recent advances in pathophysiology and treatment of spinal cord injury. Adv Physiol Educ. 2002; 26:238–255. - PubMed
-
- Dietz V, Curt A. Neurological aspects of spinal-cord repair: promises and challenges. Lancet neurol . 2006;5:688–694. - PubMed
-
- McDonald JW, Belegu V. Demyelination and remyelination after spinal cord injury. J Neurotrauma. 2006; 23:345–359. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
