Granuloma annulare and necrobiosis lipoidica with sequential occurrence in a patient: report and review of literature
- PMID: 25692078
- PMCID: PMC4325686
- DOI: 10.5826/dpc.0501a03
Granuloma annulare and necrobiosis lipoidica with sequential occurrence in a patient: report and review of literature
Abstract
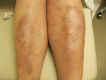
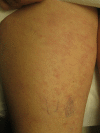
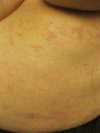
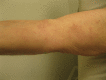
Granuloma annulare (GA) and necrobiosis lipoidica (NL) are granulomatous diseases of undetermined etiology. Rarely, both dermatoses have been reported to occur concomitantly in patients. GA and NL are characterized histologically by areas of necrobiosis of collagen. The two diseases share some common characteristics, which may suggest that these dermatoses could occur as a spectrum in some patients or possibly share a similar pathogenesis. We report on a 67-year-old Caucasian woman with a history of NL on the anterior shins that later developed lesions of GA on the breasts, trunk, and wrist. We also review the literature and discuss the characteristics of patients with concomitant GA and NL.
Keywords: concomitant; diabetes; granuloma; granuloma annulare; necrobiosis lipoidica; occurrence; review; same; sequential; simultaneous.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Concomitant granuloma annulare and necrobiosis lipoidica. Report of a case and review of the literature.Dermatologica. 1991;183(3):225-9. Dermatologica. 1991. PMID: 1743389 Review.
-
Necrobiosis lipoidica and granuloma annulare. Simultaneous occurrence in a patient.Arch Dermatol. 1982 Mar;118(3):192-3. Arch Dermatol. 1982. PMID: 7065670
-
Simultaneous occurrence of ulcerated necrobiosis lipoidica and granuloma annulare in a patient: case report.An Bras Dermatol. 2011 Sep-Oct;86(5):1007-10. doi: 10.1590/s0365-05962011000500023. An Bras Dermatol. 2011. PMID: 22147045 English, Portuguese.
-
Granuloma annulare and necrobiosis lipoidica tissue reactions as a manifestation of systemic disease.Hum Pathol. 1996 Jan;27(1):50-6. doi: 10.1016/s0046-8177(96)90137-9. Hum Pathol. 1996. PMID: 8543311
-
Update on necrobiosis lipoidica: a review of etiology, diagnosis, and treatment options.J Am Acad Dermatol. 2013 Nov;69(5):783-791. doi: 10.1016/j.jaad.2013.05.034. Epub 2013 Aug 19. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2013. PMID: 23969033 Review.
Cited by
-
Concomitant necrobiosis lipoidica and splenic abscess.J Surg Case Rep. 2019 Mar 29;2019(3):rjz088. doi: 10.1093/jscr/rjz088. eCollection 2019 Mar. J Surg Case Rep. 2019. PMID: 30949338 Free PMC article.
-
Granuloma annulare and necrobiosis lipoidica in a patient with HNF1A-MODY.Arch Endocrinol Metab. 2022 May 13;66(3):420-424. doi: 10.20945/2359-3997000000477. Epub 2022 May 12. Arch Endocrinol Metab. 2022. PMID: 35551682 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Thornsberry LA, English JC., 3rd Etiology, diagnosis, and therapeutic management of granuloma annulare: an update. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2013;14(4):279–90. - PubMed
-
- Berkson MH, Bondi EE, Margolis DJ. Ulcerated necrobiosis lipoidica diabeticorum in a patient with a history of generalized granuloma annulare. Cutis. 1994;53(2):85–86. - PubMed
-
- Souza FH, Ribeiro CF, Pereira MA, Mesquita L, Fabrício L. Simultaneous occurrence of ulcerated necrobiosis lipoidica and granuloma annulare in a patient: case report. An Bras Dermatol. 2011;86(5):1007–10. - PubMed
-
- Reid SD, Ladizinski B, Lee K, Baibergenova A, Alavi A. Update on necrobiosis lipoidica: A review of etiology, diagnosis, and treatment options. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2013;69(5):783–91. - PubMed
-
- Muhlbauer JE. Granuloma annulare. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1980;3:217–30. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
