Quantitative analysis and modeling probe polarity establishment in C. elegans embryos
- PMID: 25692585
- PMCID: PMC4336357
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bpj.2014.12.022
Quantitative analysis and modeling probe polarity establishment in C. elegans embryos
Abstract
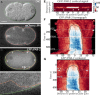
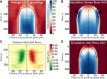
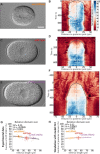
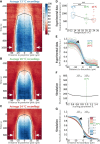
Cell polarity underlies many aspects of metazoan development and homeostasis, and relies notably on a set of PAR proteins located at the cell cortex. How these proteins interact in space and time remains incompletely understood. We performed a quantitative assessment of polarity establishment in one-cell stage Caenorhabditis elegans embryos by combining time-lapse microscopy and image analysis. We used our extensive data set to challenge and further specify an extant mathematical model. Using likelihood-based calibration, we uncovered that cooperativity is required for both anterior and posterior PAR complexes. Moreover, we analyzed the dependence of polarity establishment on changes in size or temperature. The observed robustness of PAR domain dimensions in embryos of different sizes is in agreement with a model incorporating fixed protein concentrations and variations in embryo surface/volume ratio. In addition, we quantified the dynamics of polarity establishment over most of the viable temperatures range of C. elegans. Modeling of these data suggests that diffusion of PAR proteins is the process most affected by temperature changes, although cortical flows appear unaffected. Overall, our quantitative analytical framework provides insights into the dynamics of polarity establishment in a developing system.
Copyright © 2015 Biophysical Society. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Alternative 3' UTR selection controls PAR-5 homeostasis and cell polarity in C. elegans embryos.Cell Rep. 2014 Sep 11;8(5):1380-90. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2014.08.004. Epub 2014 Sep 4. Cell Rep. 2014. PMID: 25199833
-
PAR-3 and PAR-1 inhibit LET-99 localization to generate a cortical band important for spindle positioning in Caenorhabditis elegans embryos.Mol Biol Cell. 2007 Nov;18(11):4470-82. doi: 10.1091/mbc.e07-02-0105. Epub 2007 Aug 29. Mol Biol Cell. 2007. PMID: 17761536 Free PMC article.
-
The TAO kinase KIN-18 regulates contractility and establishment of polarity in the C. elegans embryo.Dev Biol. 2013 Jan 1;373(1):26-38. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2012.10.001. Epub 2012 Oct 10. Dev Biol. 2013. PMID: 23064028
-
Regulation of Cell Polarity by PAR-1/MARK Kinase.Curr Top Dev Biol. 2017;123:365-397. doi: 10.1016/bs.ctdb.2016.11.001. Epub 2016 Dec 5. Curr Top Dev Biol. 2017. PMID: 28236972 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Gastrulation: PARtaking of the bottle.Curr Biol. 2003 Mar 18;13(6):R223-5. doi: 10.1016/s0960-9822(03)00155-6. Curr Biol. 2003. PMID: 12646146 Review.
Cited by
-
Describing the movement of molecules in reduced-dimension models.Commun Biol. 2021 Jun 7;4(1):689. doi: 10.1038/s42003-021-02200-3. Commun Biol. 2021. PMID: 34099856 Free PMC article.
-
Design principles for selective polarization of PAR proteins by cortical flows.J Cell Biol. 2023 Aug 7;222(8):e202209111. doi: 10.1083/jcb.202209111. Epub 2023 Jun 2. J Cell Biol. 2023. PMID: 37265444 Free PMC article.
-
The PAR proteins: from molecular circuits to dynamic self-stabilizing cell polarity.Development. 2017 Oct 1;144(19):3405-3416. doi: 10.1242/dev.139063. Development. 2017. PMID: 28974638 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Uncovering the balance of forces driving microtubule aster migration in C. elegans zygotes.Nat Commun. 2018 Mar 5;9(1):938. doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-03118-x. Nat Commun. 2018. PMID: 29507295 Free PMC article.
-
Cortical forces and CDC-42 control clustering of PAR proteins for Caenorhabditis elegans embryonic polarization.Nat Cell Biol. 2017 Aug;19(8):988-995. doi: 10.1038/ncb3577. Epub 2017 Jul 24. Nat Cell Biol. 2017. PMID: 28737772
References
-
- Thompson B.J. Cell polarity: models and mechanisms from yeast, worms and flies. Development. 2013;140:13–21. - PubMed
-
- Martin-Belmonte F., Perez-Moreno M. Epithelial cell polarity, stem cells and cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer. 2012;12:23–38. - PubMed
-
- Kemphues K.J., Priess J.R., Cheng N.S. Identification of genes required for cytoplasmic localization in early C. elegans embryos. Cell. 1988;52:311–320. - PubMed
-
- Gönczy P. Mechanisms of asymmetric cell division: flies and worms pave the way. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2008;9:355–366. - PubMed
-
- Motegi F., Sugimoto A. Sequential functioning of the ECT-2 RhoGEF, RHO-1 and CDC-42 establishes cell polarity in Caenorhabditis elegans embryos. Nat. Cell Biol. 2006;8:978–985. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

