Simulating the entropic collapse of coarse-grained chromosomes
- PMID: 25692586
- PMCID: PMC4336370
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bpj.2014.11.3487
Simulating the entropic collapse of coarse-grained chromosomes
Abstract
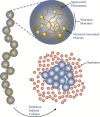
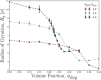
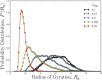
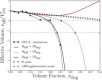
Depletion forces play a role in the compaction and decompaction of chromosomal material in simple cells, but it has remained debatable whether they are sufficient to account for chromosomal collapse. We present coarse-grained molecular dynamics simulations, which reveal that depletion-induced attraction is sufficient to cause the collapse of a flexible chain of large structural monomers immersed in a bath of smaller depletants. These simulations use an explicit coarse-grained computational model that treats both the supercoiled DNA structural monomers and the smaller protein crowding agents as combinatorial, truncated Lennard-Jones spheres. By presenting a simple theoretical model, we quantitatively cast the action of depletants on supercoiled bacterial DNA as an effective solvent quality. The rapid collapse of the simulated flexible chromosome at the predicted volume fraction of depletants is a continuous phase transition. Additional physical effects to such simple chromosome models, such as enthalpic interactions between structural monomers or chain rigidity, are required if the collapse is to be a first-order phase transition.
Copyright © 2015 Biophysical Society. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
Comment in
-
Chromosome, cell cycle, and entropy.Biophys J. 2015 Feb 17;108(4):785-786. doi: 10.1016/j.bpj.2014.12.032. Biophys J. 2015. PMID: 25692581 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Luijsterburg M.S., White M.F., Dame R.T. The major architects of chromatin: architectural proteins in bacteria, archaea and eukaryotes. Crit. Rev. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2008;43:393–418. - PubMed
-
- Arnold A., Jun S. Time scale of entropic segregation of flexible polymers in confinement: implications for chromosome segregation in filamentous bacteria. Phys. Rev. E Stat. Nonlin. Soft Matter Phys. 2007;76:031901. - PubMed
-
- Fan J., Tuncay K., Ortoleva P.J. Chromosome segregation in Escherichia coli division: a free energy-driven string model. Comput. Biol. Chem. 2007;31:257–264. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

