Awareness, treatment, and control of diabetes in Bangladesh: a nationwide population-based study
- PMID: 25692767
- PMCID: PMC4334658
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0118365
Awareness, treatment, and control of diabetes in Bangladesh: a nationwide population-based study
Abstract
Objectives: To examine awareness, treatment, and control of diabetes mellitus among the adult population in Bangladesh.
Methods: The study used data from the 2011 nationally representative Bangladesh Demographic and Health Survey (BDHS). The BDHS sample is comprised of 7,786 adults aged 35 years or older. The primary outcome variables were fasting blood glucose, diagnosis, treatment, and control of diabetes. Multilevel logistic regression models were used to identify the risk factors for diabetes awareness.
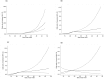
Results: Overall, age-standardized prevalence of diabetes was 9.2%. Among subjects with diabetes, 41.2% were aware of their condition, 36.9% were treated, and 14.2% controlled their condition. A significant inequality in diabetes management was found from poor to wealthy households: 18.2% to 63.2% (awareness), 15.8% to 56.6% (treatment), and 8.2% to 18.4% (control). Multilevel models suggested that participants who had a lower education and lower economic condition were less likely to be aware of their diabetes. Poor management was observed among non-educated, low-income groups, and those who lived in the northwestern region.
Conclusions: Diabetes has become a national health concern in Bangladesh; however, treatment and control are quite low. Improving detection, awareness, and treatment strategies is urgently needed to prevent the growing burden associated with diabetes.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- International Diabetes Federation (IDF) IDF Diabetes Atlas 6th Edition 2013. [cited 2014 March 01]; Available: http://www.idf.org/sites/default/files/EN_6E_Atlas_Full_0.pdf
-
- Danaei G, Finucane MM, Lu Y, Lu Y, Singh GM, Cowan MJ, et al. National, regional, and global trends in fasting plasma glucose and diabetes prevalence since 1980: systematic analysis of health examination surveys and epidemiological studies with 370 country-years and 2 7 million participants. Lancet 2011; 378: 31–40. 10.1016/S0140-6736(11)60679-X - DOI - PubMed
-
- Mendis S, Puska P, Norrving B, World Health Organization, World Heart Federation, World Stroke Organization. Global atlas on cardiovascular disease prevention and control. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2011.
-
- Guariguata L, Whiting D, Hambleton I, Beagley J, Linnenkamp U, Shaw J. Global estimates of diabetes prevalence for 2013 and projections for 2035 for the IDF Diabetes Atlas. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 2013. - PubMed
-
- Lim SS, Vos T, Flaxman AD, Danaei G, Shibuya K, Adair-Rohani H, et al. A comparative risk assessment of burden of disease and injury attributable to 67 risk factors and risk factor clusters in 21 regions, 1990–2010: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2010. Lancet 2013; 380: 2224–60. - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

