Statistical methods for handling unwanted variation in metabolomics data
- PMID: 25692814
- PMCID: PMC4544854
- DOI: 10.1021/ac502439y
Statistical methods for handling unwanted variation in metabolomics data
Abstract
Metabolomics experiments are inevitably subject to a component of unwanted variation, due to factors such as batch effects, long runs of samples, and confounding biological variation. Although the removal of this unwanted variation is a vital step in the analysis of metabolomics data, it is considered a gray area in which there is a recognized need to develop a better understanding of the procedures and statistical methods required to achieve statistically relevant optimal biological outcomes. In this paper, we discuss the causes of unwanted variation in metabolomics experiments, review commonly used metabolomics approaches for handling this unwanted variation, and present a statistical approach for the removal of unwanted variation to obtain normalized metabolomics data. The advantages and performance of the approach relative to several widely used metabolomics normalization approaches are illustrated through two metabolomics studies, and recommendations are provided for choosing and assessing the most suitable normalization method for a given metabolomics experiment. Software for the approach is made freely available.
Figures

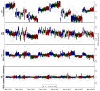

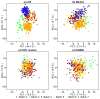

References
-
- Monteiro MS, Carvalho M, Bastos ML, Guedes de Pinho P. Current medicinal chemistry. 2013;20:257–71. - PubMed
-
- Armitage EG, Barbas C. Journal of pharmaceutical and biomedical analysis. 2014;87:1–11. - PubMed
-
- De Livera AM, Olshansky M, Speed TP. Methods in molecular biology (Clifton, NJ) 2013;1055:291–307. - PubMed
-
- Dunn WB, Broadhurst D, Begley P, Zelena E, Francis-McIntyre S, Anderson N, Brown M, Knowles JD, Halsall A, Haselden JN, Nicholls AW, Wilson ID, Kell DB, Goodacre R. Nature protocols. 2011;6:1060–1083. - PubMed
-
- Wang S-Y, Kuo C-H, Tseng YJ. Analytical chemistry. 2013:1037–46. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

