Characterization of a recombinant humanized anti-cocaine monoclonal antibody and its Fab fragment
- PMID: 25692880
- PMCID: PMC4514192
- DOI: 10.4161/21645515.2014.990856
Characterization of a recombinant humanized anti-cocaine monoclonal antibody and its Fab fragment
Abstract
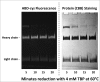
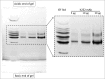
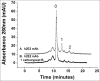
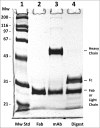
Variations of post-translational modifications are important for stability and in vivo behavior of therapeutic antibodies. A recombinant humanized anti-cocaine monoclonal antibody (h2E2) was characterized for heterogeneity of N-linked glycosylation and disulfide bonds. In addition, charge heterogeneity, which is partially due to the presence or absence of C-terminal lysine on the heavy chains, was examined. For cocaine overdose therapy, Fab fragments may be therapeutic, and thus, a simplified method of generation, purification, and characterization of the Fab fragment generated by Endoproteinase Lys-C digestion was devised. Both the intact h2E2 antibody and purified Fab fragments were analyzed for their affinities for cocaine and 2 of its metabolites, benzoylecgonine and cocaethylene, by fluorescence quenching of intrinsic antibody tyrosine and tryptophan fluorescence resulting from binding of these drugs. Binding constants obtained from fluorescence quenching measurements are in agreement with recently published radioligand and ELISA binding assays. The dissociation constants determined for the h2E2 monoclonal and its Fab fragment are approximately 1, 5, and 20 nM for cocaethylene, cocaine, and benzoylecgonine, respectively. Tryptophan fluorescence quenching (emission at 330 nm) was measured after either excitation of tyrosine and tryptophan (280 nm) or selective excitation of tryptophan alone (295 nm). More accurate binding constants are obtained using tryptophan selective excitation at 295 nm, likely due to interfering absorption of cocaine and metabolites at 280 nm. These quenching results are consistent with multiple tryptophan and tyrosine residues in or near the predicted binding location of cocaine in a previously published 3-D model of this antibody's variable region.
Keywords: ABD-F, 7-fluorobenz-2-oxa-1, 3-diazole-4-sulfonamide; ADCC, antibody-dependent cell mediated cytotoxicity; BE, benzoylecgonine; CDR, complementarity determining regions; CE, cocaethylene; CHO, Chinese hamster ovary; ELISA, enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay; Endo H, endoglycosidase H; Endo Lys-C, lysyl endoproteinase; Fab fragment; Fab, fragment; Fc, fragment, crystallizable; HPLC, high performance liquid chromatography; IEF, isoelectric focusing; KD, dissociation constant; MES, 2-(N-morpholino)ethanesulfonic acid; MOPS, 3-(N-morpholino)propanesulfonic acid; NEPHGE, non-equilibrium pH gel electrophoresis; PNGase-F, peptide N-glycosidase F; SCX, strong cation exchange; TBP, tributylphosphine; TBS, tris-buffered saline; antigen-binding; cocaine; fluorescence quenching, heterogeneity; h2E2, humanized monoclonal antibody against cocaine; high performance ion exchange chromatography; ligand binding; mAb, monoclonal antibody; monoclonal antibody; non-equilibrium pH gel electrophoresis.
Figures

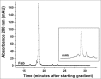
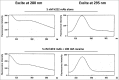
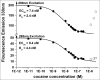
References
-
- Beck A, Wagner-Rousset E, Ayoub D, Van Dorsselaer A, Sanglier-Cianferani S. Characterization of therapeutic antibodies and related products. Anal Chem 2013; 85:715-36; PMID:23134362; http://dx.doi.org/ 10.1021/ac3032355 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Liu H, Gaza-Bulseco G, Faldu D, Chumsae C, Sun J. Heterogeneity of monoclonal antibodies. J Pharm Sci 2008; 97:2426-47; PMID:17828757; http://dx.doi.org/ 10.1002/jps.21180 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Kayser V, Chennamsetty N, Voynov V, Forrer K, Helk B, Trout BL. Glycosylation influences on the aggregation propensity of therapeutic monoclonal antibodies. Biotechnol J 2011; 6:38-44; PMID:20949542; http://dx.doi.org/ 10.1002/biot.201000091 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Broussas M, Broyer L, Goetsch L. Evaluation of antibody-dependent cell cytotoxicity using lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) measurement. Methods Mol Biol 2013; 988:305-17; PMID:23475728; http://dx.doi.org/ 10.1007/978-1-62703-327-5_19 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Goetze AM, Liu YD, Zhang Z, Shah B, Lee E, Bondarenko PV, Flynn GC. High-mannose glycans on the Fc region of therapeutic IgG antibodies increase serum clearance in humans. Glycobiology 2011; 21:949-59; PMID:21421994; http://dx.doi.org/ 10.1093/glycob/cwr027 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
