RIPK3 promotes cell death and NLRP3 inflammasome activation in the absence of MLKL
- PMID: 25693118
- PMCID: PMC4346630
- DOI: 10.1038/ncomms7282
RIPK3 promotes cell death and NLRP3 inflammasome activation in the absence of MLKL
Abstract
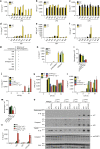
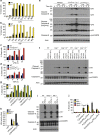
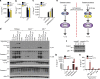
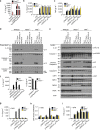
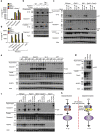
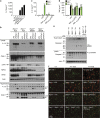
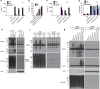
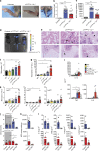
RIPK3 and its substrate MLKL are essential for necroptosis, a lytic cell death proposed to cause inflammation via the release of intracellular molecules. Whether and how RIPK3 might drive inflammation in a manner independent of MLKL and cell lysis remains unclear. Here we show that following LPS treatment, or LPS-induced necroptosis, the TLR adaptor protein TRIF and inhibitor of apoptosis proteins (IAPs: X-linked IAP, cellular IAP1 and IAP2) regulate RIPK3 and MLKL ubiquitylation. Hence, when IAPs are absent, LPS triggers RIPK3 to activate caspase-8, promoting apoptosis and NLRP3-caspase-1 activation, independent of RIPK3 kinase activity and MLKL. In contrast, in the absence of both IAPs and caspase-8, RIPK3 kinase activity and MLKL are essential for TLR-induced NLRP3 activation. Consistent with in vitro experiments, interleukin-1 (IL-1)-dependent autoantibody-mediated arthritis is exacerbated in mice lacking IAPs, and is reduced by deletion of RIPK3, but not MLKL. Therefore RIPK3 can promote NLRP3 inflammasome and IL-1β inflammatory responses independent of MLKL and necroptotic cell death.
Conflict of interest statement
J.S. and D.L.V. are on the Scientific Advisory Board of TetraLogic Pharmaceuticals. Y.M., C.A.B. and S.M.C. are employees of TetraLogic Pharmaceuticals. All other authors declare no other competing financial interests.
Figures

References
-
- Bertrand M. J. et al.. cIAP1 and cIAP2 facilitate cancer cell survival by functioning as E3 ligases that promote RIP1 ubiquitination. Mol. Cell 30, 689–700 (2008). - PubMed
-
- Haas T. L. et al.. Recruitment of the linear ubiquitin chain assembly complex stabilizes the TNF-R1 signaling complex and is required for TNF-mediated gene induction. Mol. Cell 36, 831–844 (2009). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

