Systemic delivery of microRNA-101 potently inhibits hepatocellular carcinoma in vivo by repressing multiple targets
- PMID: 25693145
- PMCID: PMC4334495
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1004873
Systemic delivery of microRNA-101 potently inhibits hepatocellular carcinoma in vivo by repressing multiple targets
Erratum in
-
Correction: Systemic Delivery of MicroRNA-101 Potently Inhibits Hepatocellular Carcinoma In Vivo by Repressing Multiple Targets.PLoS Genet. 2021 Dec 8;17(12):e1009960. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1009960. eCollection 2021 Dec. PLoS Genet. 2021. PMID: 34879067 Free PMC article.
Abstract
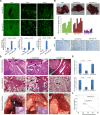
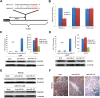
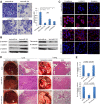
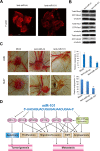
Targeted therapy based on adjustment of microRNA (miRNA)s activity takes great promise due to the ability of these small RNAs to modulate cellular behavior. However, the efficacy of miR-101 replacement therapy to hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) remains unclear. In the current study, we first observed that plasma levels of miR-101 were significantly lower in distant metastatic HCC patients than in HCCs without distant metastasis, and down-regulation of plasma miR-101 predicted a worse disease-free survival (DFS, P<0.05). In an animal model of HCC, we demonstrated that systemic delivery of lentivirus-mediated miR-101 abrogated HCC growth in the liver, intrahepatic metastasis and distant metastasis to the lung and to the mediastinum, resulting in a dramatic suppression of HCC development and metastasis in mice without toxicity and extending life expectancy. Furthermore, enforced overexpression of miR-101 in HCC cells not only decreased EZH2, COX2 and STMN1, but also directly down-regulated a novel target ROCK2, inhibited Rho/Rac GTPase activation, and blocked HCC cells epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) and angiogenesis, inducing a strong abrogation of HCC tumorigenesis and aggressiveness both in vitro and in vivo. These results provide proof-of-concept support for systemic delivery of lentivirus-mediated miR-101 as a powerful anti-HCC therapeutic modality by repressing multiple molecular targets.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures

Similar articles
-
MicroRNA-1296 inhibits metastasis and epithelial-mesenchymal transition of hepatocellular carcinoma by targeting SRPK1-mediated PI3K/AKT pathway.Mol Cancer. 2017 Jun 12;16(1):103. doi: 10.1186/s12943-017-0675-y. Mol Cancer. 2017. PMID: 28606154 Free PMC article.
-
The putative tumour suppressor microRNA-124 modulates hepatocellular carcinoma cell aggressiveness by repressing ROCK2 and EZH2.Gut. 2012 Feb;61(2):278-89. doi: 10.1136/gut.2011.239145. Epub 2011 Jun 14. Gut. 2012. PMID: 21672940
-
Inhibitions of epithelial to mesenchymal transition and cancer stem cells-like properties are involved in miR-148a-mediated anti-metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma.Mol Carcinog. 2014 Dec;53(12):960-9. doi: 10.1002/mc.22064. Epub 2013 Jul 17. Mol Carcinog. 2014. PMID: 23861222
-
MicroRNAs Involved in Metastasis of Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Target Candidates, Functionality and Efficacy in Animal Models and Prognostic Relevance.Cancer Genomics Proteomics. 2020 Jan-Feb;17(1):1-21. doi: 10.21873/cgp.20163. Cancer Genomics Proteomics. 2020. PMID: 31882547 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Role of the MiR-181 Family in Hepatocellular Carcinoma.Cells. 2024 Jul 31;13(15):1289. doi: 10.3390/cells13151289. Cells. 2024. PMID: 39120319 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
MicroRNA-101 reverses temozolomide resistance by inhibition of GSK3β in glioblastoma.Oncotarget. 2016 Nov 29;7(48):79584-79595. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.12861. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 27792996 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA-101 regulated transcriptional modulator SUB1 plays a role in prostate cancer.Oncogene. 2016 Dec 8;35(49):6330-6340. doi: 10.1038/onc.2016.164. Epub 2016 Jun 6. Oncogene. 2016. PMID: 27270442 Free PMC article.
-
Technological advances in precision medicine and drug development.Expert Rev Precis Med Drug Dev. 2016;1(3):331-343. doi: 10.1080/23808993.2016.1176527. Epub 2016 May 5. Expert Rev Precis Med Drug Dev. 2016. PMID: 27622214 Free PMC article.
-
An NF90/NF110-mediated feedback amplification loop regulates dicer expression and controls ovarian carcinoma progression.Cell Res. 2018 May;28(5):556-571. doi: 10.1038/s41422-018-0016-8. Epub 2018 Mar 21. Cell Res. 2018. PMID: 29563539 Free PMC article.
-
The Epigenetic Modulation of Cancer and Immune Pathways in Hepatitis B Virus-Associated Hepatocellular Carcinoma: The Influence of HBx and miRNA Dysregulation.Front Immunol. 2021 Apr 29;12:661204. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.661204. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 33995383 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Pisani P, Parkin DM, Bray F, Ferlay J (1999) Erratum: Estimates of the worldwide mortality from 25 cancers in 1990. Int. J. Cancer, 83, 18–29 (1999). Int J Cancer 83: 870–873. - PubMed
-
- Yang X, Zhang XF, Lu X, Jia HL, Liang L, et al. (2013) MicroRNA-26a suppresses angiogenesis in human hepatocellular carcinoma by targeting hepatocyte growth factor-cMet pathway. Hepatology 59(5):1874–85. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

