Spinal stimulation of the upper lumbar spinal cord modulates urethral sphincter activity in rats after spinal cord injury
- PMID: 25694482
- PMCID: PMC6189748
- DOI: 10.1152/ajprenal.00573.2014
Spinal stimulation of the upper lumbar spinal cord modulates urethral sphincter activity in rats after spinal cord injury
Abstract
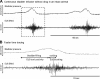
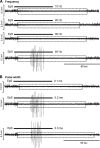
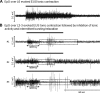
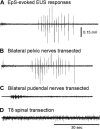
After spinal cord injury (SCI), the neurogenic bladder is observed to develop asynchronous bladder and external urethral sphincter (EUS) contractions in a condition known as detrusor-sphincter dyssnergia (DSD). Activation of the EUS spinal controlling center located at the upper lumbar spinal cord may contribute to reduce EUS dyssynergic contractions and decrease urethral resistance during voiding. However, this mechanism has not been well studied. This study aimed at evaluating the effects of epidural stimulation (EpS) over the spinal EUS controlling center (L3) in combination with a serotonergic receptor agonist on EUS relaxation in naive rats and chronic (6-8 wk) T8 SCI rats. Cystometrogram and EUS electromyography (EMG) were obtained before and after the intravenous administration of 5HT-1A receptor agonist and antagonist. The latency, duration, frequency, amplitude, and area under curve of EpS-evoked EUS EMG responses were analyzed. EpS on L3 evoked an inhibition of EUS tonic contraction and an excitation of EUS intermittent bursting/relaxation correlating with urine expulsion in intact rats. Combined with a 5HT-1A receptor agonist, EpS on L3 evoked a similar effect in chronic T8 SCI rats to reduce urethral contraction (resistance). This study examined the effect of facilitating the EUS spinal controlling center to switch between urine storage and voiding phases by using EpS and a serotonergic receptor agonist. This novel approach of applying EpS on the EUS controlling center modulates EUS contraction and relaxation as well as reduces urethral resistance during voiding in chronic SCI rats with DSD.
Keywords: electromyography; epidural stimulation; serotonergic receptors; urethral resistance.
Copyright © 2015 the American Physiological Society.
Figures
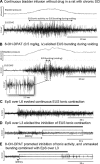
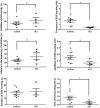
References
-
- Birder LA, Roppolo JR, Iadarola MJ, de Groat WC. Electrical stimulation of visceral afferent pathways in the pelvic nerve increases c-fos in the rat lumbosacral spinal cord. Neurosci Lett : 193–196, 1999. - PubMed
-
- Cardenas DD, Hooton TM. Urinary tract infection in persons with spinal cord injury. Arch Phys Med Rehabil : 272–280, 1995. - PubMed
-
- Chang HY, Cheng CL, Chen JJ, de Groat WC. Serotonergic drugs and spinal cord transections at different segmental levels indicate that different spinal circuits are involved in tonic and bursting external urethral sphincter activity in rats. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol : F1044–F1053, 2007. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

