Drug persistence with rivaroxaban therapy in atrial fibrillation patients-results from the Dresden non-interventional oral anticoagulation registry
- PMID: 25694537
- PMCID: PMC4381834
- DOI: 10.1093/europace/euu319
Drug persistence with rivaroxaban therapy in atrial fibrillation patients-results from the Dresden non-interventional oral anticoagulation registry
Abstract
Aims: Worldwide, rivaroxaban is increasingly used for stroke prevention in atrial fibrillation (SPAF) but little is known about the rates of or reasons for rivaroxaban discontinuations in daily care. Using data from a prospective, non-interventional oral anticoagulation (NOAC) registry, we analysed rivaroxaban treatment persistence.
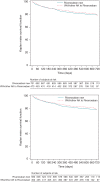
Methods and results: Persistence with rivaroxaban in SPAF was assessed in an ongoing, prospective, non-interventional registry of >2600 NOAC patients from daily care using the Kaplan-Meier time-to-first-event analysis. Reasons for and management of rivaroxaban discontinuation were assessed. Potential baseline risk factors for treatment discontinuation were evaluated using Cox regression analysis. Between October 2011 and April 2014, 1204 rivaroxaban SPAF patients were enrolled [39.3% switched from vitamin K antagonists (VKAs) and 60.7% newly treated patients]. Of these, 223 patients (18.5%) stopped rivaroxaban during follow-up (median 544 days), which translates into a discontinuation rate of 13.6 (95% CI 11.8-15.4) per 100 patient-years. Most common reasons for treatment discontinuations were bleeding complications (30% of all discontinuations), followed by other side-effects (24.2%) and diagnosis of stable sinus rhythm (9.9%). A history of chronic heart failure (HR 1.43; 95% CI 1.09-1.87; P = 0.009) or diabetes (HR 1.39; 95% CI 1.06-1.82; P = 0.018) were the only statistically significant baseline risk factors for rivaroxaban discontinuation. After discontinuation of rivaroxaban, patients received antiplatelet therapy (31.8%), VKA (24.2%), another NOAC (18.4%), heparin (9.9%), or nothing (15.7%).
Conclusion: Our data indicate that overall persistence with rivaroxaban therapy is high, with a discontinuation rate of ∼15% in the first year of treatment and few additional discontinuations thereafter.
Keywords: Anticoagulants; Atrial fibrillation; NOAC; Persistence; Rivaroxaban.
© The Author 2015. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the European Society of Cardiology.
Figures
Comment in
-
Optimizing stroke prevention in atrial fibrillation: better adherence and compliance from patients and physicians leads to better outcomes.Europace. 2015 Apr;17(4):507-8. doi: 10.1093/europace/euv041. Europace. 2015. PMID: 25833879 No abstract available.
-
Independent data about the safety and efficacy of rivaroxaban for prevention of stroke/embolism are needed: Author reply.Europace. 2016 Jan;18(1):156-8. doi: 10.1093/europace/euv286. Epub 2015 Dec 30. Europace. 2016. PMID: 26718531 No abstract available.
-
Independent data about the safety and efficacy of rivaroxaban for prevention of stroke/embolism are needed.Europace. 2016 Jan;18(1):156. doi: 10.1093/europace/euv277. Epub 2015 Dec 30. Europace. 2016. PMID: 26718534 No abstract available.
References
-
- Gallagher AM, Rietbrock S, Plumb J, van Staa TP. Initiation and persistence of warfarin or aspirin in patients with chronic atrial fibrillation in general practice: do the appropriate patients receive stroke prophylaxis? J Thromb Haemost 2008;6:1500–6. - PubMed
-
- Hylek EM, Evans-Molina C, Shea C, Henault LE, Regan S. Major hemorrhage and tolerability of warfarin in the first year of therapy among elderly patients with atrial fibrillation. Circulation 2007;115:2689–96. - PubMed
-
- De Breucker S, Herzog G, Pepersack T. Could geriatric characteristics explain the under-prescription of anticoagulation therapy for older patients admitted with atrial fibrillation? A retrospective observational study. Drugs Aging 2010;27:807–13. - PubMed
-
- Patel MR, Mahaffey KW, Garg J, Pan G, Singer DE, Hacke W, et al. Rivaroxaban versus warfarin in nonvalvular atrial fibrillation. N Engl J Med 2011;365:883–91. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous