Image reconstruction of the absorption coefficients with l 1-norm minimization from photoacoustic measurements
- PMID: 25694957
- PMCID: PMC4312303
- DOI: 10.3978/j.issn.2223-4292.2014.11.22
Image reconstruction of the absorption coefficients with l 1-norm minimization from photoacoustic measurements
Abstract
Background: The photoacoustic (PA) imaging by considering light propagation into image reconstruction process can provide quantitative information of photon absorbers, such as hemoglobin and exogenous dyes, and to improve their imaging contrasts.
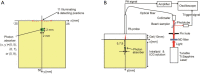
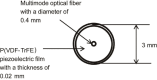
Methods: A 2D image reconstruction of the distribution of the light absorption coefficient from the PA measurements with light source and ultrasound transducer placed at the identical position was tested. The PA pressures were formulated with the PA wave equation and the photon diffusion equation. The relation between the PA pressure and the absorption coefficient was linearized. The image reconstruction was carried out by minimizing the squared error between the measured and calculated PA signals. The l 1-norm of the reconstructed image was simultaneously minimized to improve the localization of the reconstructed target in the image. The image reconstruction with the l 1-norm minimization was compared to that with the Tikhonov regularization by numerical simulation and phantom experiment. In phantom experiment, an aqueous solution of the intralipid and the indocyanine green was used as the measured object. The PA probe had optical fiber for illumination and piezoelectric film for detection placed at the identical position.
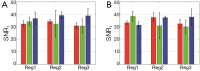
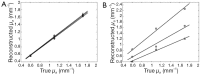
Results: The l 1-norm minimization reconstructed more localized target than the Tikhonov regularization.
Conclusions: The l 1-norm minimization is useful for the sparse PA image reconstruction.
Keywords: Absorption coefficient; image reconstruction; inverse problem; photoacoustic (PA) imaging.
Figures



References
-
- Wang S, Shibahara N, Kuramashi D, Okawa S, Kakuta N, Okada E, Maki A, Yamada Y.Effect of Spatial Variation of Skull and Cerebrospinal Fluid Layer on Optical Mapping of Brain Activities. Opt Rev 2010;17:410-20.
-
- Gibson AP, Hebden JC, Arridge SR. Recent advances in diffuse optical imaging. Phys Med Biol 2005;50:R1-43. - PubMed
-
- Fukuzawa R, Okawa S, Matsuhashi S, et al. Reduction of image artifacts induced by change in the optode coupling in time-resolved diffuse optical tomography. J Biomed Opt 2011;16:116022. - PubMed
-
- Yates T, Hebden JC, Gibson A, Everdell N, Arridge SR, Douek M. Optical tomography of the breast using a multi-channel time-resolved imager. Phys Med Biol 2005;50:2503-17. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
