Accuracy of pepsinogens for early diagnosis of atrophic gastritis and gastric cancer in Iranian population
- PMID: 25695008
- PMCID: PMC4322333
Accuracy of pepsinogens for early diagnosis of atrophic gastritis and gastric cancer in Iranian population
Abstract
Background: Currently, non-invasive methods for screening atrophic gastritis and gastric cancer are lacking. The purpose of this study was to evaluate the value of serological parameters including serum pepsinogen I (PGI), pepsinogen II (PGII) and pepsinogen I: II ratio for the screening atrophic gastritis and gastric cancer.
Methods: The study population consisted of 132 dyspeptic patients who had undergone upper endoscopy with biopsy. Blood samples for ELISA assays of serum PGI, PGII and IgG antibodies against Helicobacter pylori were drawn. Comparison between the two groups was done by Student's t- test, and Mann Whitney test. Cut-off points were calculated using receiver operating curves (ROC).
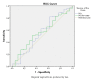
Results: Mean (±SD) age of the study population was 51.4 (±15.5) years. Values of PGI and PG ratio decreased significantly in the atrophic gastritis as compared with the control group (p<0.05). Values of PG and PG ratio didn't show any significant difference between the gastric cancer and control group (p>0.05). For patients with atrophic gastritis, the area under the ROC for PGI was 0.639 (95% CI:0.538-0.741, p=0.008) in which the best cut-off value was 40μg/L (sensitivity 90%, specificity 67%, accuracy 69%, negative predictive value 92%, YI : 0.429). The area under the ROC for PG ratio was 0.711 (95% CI: 0.617-0.806, p=0.0001) and the best cut-off value was 8 (sensitivity 71%, specificity 71%, accuracy 71%, negative predictive value 86%,YI : 0.431).
Conclusion: It seems that PGI, PGI: PGII ratio is potential biomarkers for screening atrophic gastritis with high sensitivity, specificity, accuracy and negative predictive value. Serology could be used as a screening method for the detection of precancerous states due to its convenience, relative low cost and safety.
Keywords: Atrophic gastritis; Biomarkers; Gastric cancer; Pepsinogens.
Similar articles
-
Diagnosis of atrophic body gastritis in Chinese patients by measuring serum pepsinogen.Chin J Dig Dis. 2004;5(1):22-7. doi: 10.1111/j.1443-9573.2004.00148.x. Chin J Dig Dis. 2004. PMID: 15612668
-
[Clinical utility of serum pepsinogen levels as a screening test of atrophic gastritis].Korean J Lab Med. 2008 Jun;28(3):201-6. doi: 10.3343/kjlm.2008.28.3.201. Korean J Lab Med. 2008. PMID: 18594172 Korean.
-
Screening of atrophic gastritis and gastric cancer by serum pepsinogen, gastrin-17 and Helicobacter pylori immunoglobulin G antibodies.J Dig Dis. 2007 Feb;8(1):15-22. doi: 10.1111/j.1443-9573.2007.00271.x. J Dig Dis. 2007. PMID: 17261130
-
Using serum pepsinogens wisely in a clinical practice.J Dig Dis. 2007 Feb;8(1):8-14. doi: 10.1111/j.1443-9573.2007.00278.x. J Dig Dis. 2007. PMID: 17261129 Review.
-
[Helicobacter pylori and the development of atrophic gastritis].Nihon Rinsho. 1993 Dec;51(12):3231-5. Nihon Rinsho. 1993. PMID: 8283639 Review. Japanese.
Cited by
-
The potential value of serum pepsinogen for the diagnosis of atrophic gastritis among the health check-up populations in China: a diagnostic clinical research.BMC Gastroenterol. 2017 Jul 20;17(1):88. doi: 10.1186/s12876-017-0641-6. BMC Gastroenterol. 2017. PMID: 28728545 Free PMC article.
-
Significance of Serum Pepsinogens as a Biomarker for Gastric Cancer and Atrophic Gastritis Screening: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.PLoS One. 2015 Nov 10;10(11):e0142080. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0142080. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26556485 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical Value of Combined Detection of Serum sTim-3 and Pepsinogen for Gastric Cancer Diagnosis.Cancer Manag Res. 2021 Oct 9;13:7759-7769. doi: 10.2147/CMAR.S328312. eCollection 2021. Cancer Manag Res. 2021. PMID: 34675671 Free PMC article.
-
Serum pepsinogen levels in different regions of China and its influencing factors: a multicenter cross-sectional study.BMC Gastroenterol. 2021 Jun 12;21(1):264. doi: 10.1186/s12876-021-01794-6. BMC Gastroenterol. 2021. PMID: 34118868 Free PMC article.
-
Long noncoding RNAs as auxiliary biomarkers for gastric cancer screening: A pooled analysis of individual studies.Oncotarget. 2016 May 3;7(18):25791-800. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.8268. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 27015554 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Jemal A, Thomas A, Murray T, Thun M. Cancer statistics, 2002. CA Cancer J Clin. 2002;52:23–47. - PubMed
-
- Lee KJ, Inoue M, Otani T, Iwasaki M, Sasazuki S, Tsugane S. Gastric cancer screening and subsequent risk of gastric cancer: a large-scale population-based cohort study, with a 13-year follow-up in Japan. Int J Cancer. 2006;1(118)):2315–2321. - PubMed
-
- Sipponen P, Härkönen M. et al. Diagnosis of atrophic gastritis from a serum sample. Clin Lab. 2002;48:505–15. - PubMed
-
- Suovaniemi O, Härkönen M. et al. Diagnosis of atrophic gastritis from a serum sample. Jordan Med J. 2002;36:117–21.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources