Does kidney transplantation with deceased or living donor affect graft survival?
- PMID: 25695017
- PMCID: PMC4317718
- DOI: 10.5812/numonthly.12182
Does kidney transplantation with deceased or living donor affect graft survival?
Abstract
Background: There are growing numbers of patients with end-stage renal disease globally at an unexpected rate. Today, the most serious challenge in transplantation is organ shortage; hence, using deceased donor is increasingly encouraged.
Objectives: The aim of the study was to investigate the differences in survival rates between kidney transplant recipients with deceased donor and living donor.
Patients and methods: In a retrospective cohort study, 218 patients who had undergone kidney transplantation in our institute from April 2008 to September 2010 were recruited. Demographics and post-transplantation follow-up data including immunosuppression regimens, rejection episodes, and survival rates were evaluated. The patients were assigned to two groups according to the donor kidney transplantation: group I, living donor kidney transplants; and group II, deceased donor kidney transplants.
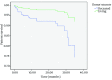
Results: Although there were no significant differences in one-year survival rates of patient and graft between study groups, three-years survival rates of patient and graft were significantly longer in living donor kidney transplants in comparison with the deceased donor kidney recipients (P = 0.006 and P = 0.004, respectively). In Cox-regression model after adjusting for other confounding factors such as age, sex, diabetes mellitus, and first- or second-time transplantation, overall patient and graft survivals were also significantly shorter in deceased kidney transplantation than those who received kidney from a living donor (HR, 3.5; 95% CI, 1.2-10.4; and P = 0.02 for patient survival; and HR, 5.4; 95% CI, 1.5-19.5; and P = 0.009 for graft survival).
Conclusions: We found acceptable short-term survival in both groups; however, living donor recipients continue to have better long-term patient and graft survival rates.
Keywords: Donor; Kidney Transplantations; Living Donor; Survival.
Figures
References
-
- Nafar M, Mousavi SM, Mahdavi-Mazdeh M, Pour-Reza-Gholi F, Firoozan A, Einollahi B, et al. Burden of chronic kidney disease in Iran: a screening program is of essential need. Iran J Kidney Dis. 2008;2(4):183–92. - PubMed
-
- Aghighi M, Mahdavi-Mazdeh M, Zamyadi M, Heidary Rouchi A, Rajolani H, Nourozi S. Changing epidemiology of end-stage renal disease in last 10 years in Iran. Iran J Kidney Dis. 2009;3(4):192–6. - PubMed
-
- Perico N, Plata R, Anabaya A, Codreanu I, Schieppati A, Ruggenenti P, et al. Strategies for national health care systems in emerging countries: the case of screening and prevention of renal disease progression in Bolivia. Kidney Int Suppl. 2005;(97):S87–94. doi: 10.1111/j.1523-1755.2005.09715.x. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous