Guanine-modified inhibitory oligonucleotides efficiently impair TLR7- and TLR9-mediated immune responses of human immune cells
- PMID: 25695778
- PMCID: PMC4335036
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0116703
Guanine-modified inhibitory oligonucleotides efficiently impair TLR7- and TLR9-mediated immune responses of human immune cells
Abstract
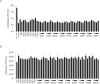
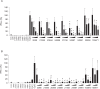
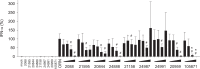
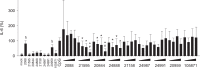
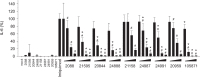
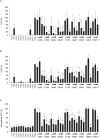
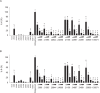
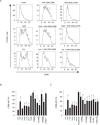
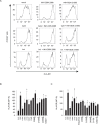
Activation of TLR7 and TLR9 by endogenous RNA- or DNA-containing ligands, respectively, is thought to contribute to the complicated pathophysiology of systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE). These ligands induce the release of type-I interferons by plasmacytoid dendritic cells and autoreactive antibodies by B-cells, both responses being key events in perpetuating SLE. We recently described the development of inhibitory oligonucleotides (INH-ODN), which are characterized by a phosphorothioate backbone, a CC(T)XXX3-5GGG motif and a chemical modification of the G-quartet to avoid the formation of higher order structures via intermolecular G-tetrads. These INH-ODNs were equally or significantly more efficient to impair TLR7- and TLR9-stimulated murine B-cells, macrophages, conventional and plasmacytoid dendritic cells than the parent INH-ODN 2088, which lacks G-modification. Here, we evaluate the inhibitory/therapeutic potential of our set of G-modified INH-ODN on human immune cells. We report the novel finding that G-modified INH-ODNs efficiently inhibited the release of IFN-α by PBMC stimulated either with the TLR7-ligand oligoribonucleotide (ORN) 22075 or the TLR9-ligand CpG-ODN 2216. G-modification of INH-ODNs significantly improved inhibition of IL-6 release by PBMCs and purified human B-cells stimulated with the TLR7-ligand imiquimod or the TLR9-ligand CpG-ODN 2006. Furthermore, inhibition of B-cell activation analyzed by expression of activation markers and intracellular ATP content was significantly improved by G-modification. As observed with murine B-cells, high concentrations of INH-ODN 2088 but not of G-modified INH-ODNs stimulated IL-6 secretion by PBMCs in the absence of TLR-ligands thus limiting its blocking efficacy. In summary, G-modification of INH-ODNs improved their ability to impair TLR7- and TLR9-mediated signaling in those human immune cells which are considered as crucial in the pathophysiology of SLE.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
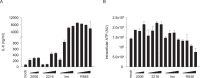
Similar articles
-
Guanine modification of inhibitory oligonucleotides potentiates their suppressive function.J Immunol. 2013 Sep 15;191(6):3240-53. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1300706. Epub 2013 Aug 21. J Immunol. 2013. PMID: 23966630
-
DNA-like class R inhibitory oligonucleotides (INH-ODNs) preferentially block autoantigen-induced B-cell and dendritic cell activation in vitro and autoantibody production in lupus-prone MRL-Fas(lpr/lpr) mice in vivo.Arthritis Res Ther. 2009;11(3):R79. doi: 10.1186/ar2710. Epub 2009 May 28. Arthritis Res Ther. 2009. PMID: 19476613 Free PMC article.
-
Aggregation and secondary loop structure of oligonucleotides do not determine their ability to inhibit TLR9.Int Immunopharmacol. 2011 Aug;11(8):1032-7. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2011.02.023. Epub 2011 Mar 2. Int Immunopharmacol. 2011. PMID: 21376154 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting Toll-like receptor signaling in plasmacytoid dendritic cells and autoreactive B cells as a therapy for lupus.Arthritis Res Ther. 2006;8(1):203. doi: 10.1186/ar1888. Epub 2006 Jan 10. Arthritis Res Ther. 2006. PMID: 16542467 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Modulating toll-like receptor 7 and 9 responses as therapy for allergy and autoimmunity.Curr Allergy Asthma Rep. 2012 Feb;12(1):8-17. doi: 10.1007/s11882-011-0233-4. Curr Allergy Asthma Rep. 2012. PMID: 22086297 Review.
Cited by
-
The role of extracellular DNA in COVID-19: Clues from inflamm-aging.Ageing Res Rev. 2021 Mar;66:101234. doi: 10.1016/j.arr.2020.101234. Epub 2020 Dec 13. Ageing Res Rev. 2021. PMID: 33321254 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The multiple functions of miR-574-5p in the neuroblastoma tumor microenvironment.Front Pharmacol. 2023 Sep 4;14:1183720. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1183720. eCollection 2023. Front Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 37731742 Free PMC article.
-
Rhinovirus stimulated IFN-α production: how important are plasmacytoid DCs, monocytes and endosomal pH?Clin Transl Immunology. 2015 Oct 30;4(10):e46. doi: 10.1038/cti.2015.27. eCollection 2015 Oct. Clin Transl Immunology. 2015. PMID: 26682054 Free PMC article.
-
Agonist and antagonist ligands of toll-like receptors 7 and 8: Ingenious tools for therapeutic purposes.Eur J Med Chem. 2020 May 1;193:112238. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2020.112238. Epub 2020 Mar 17. Eur J Med Chem. 2020. PMID: 32203790 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Inhibition of Toll-Like Receptor Signaling as a Promising Therapy for Inflammatory Diseases: A Journey from Molecular to Nano Therapeutics.Front Physiol. 2017 Jul 19;8:508. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2017.00508. eCollection 2017. Front Physiol. 2017. PMID: 28769820 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Baccala R, Hoebe K, Kono DH, Beutler B, Theofilopoulos AN (2007) TLR-dependent and TLR-independent pathways of type I interferon induction in systemic autoimmunity. Nat Med 13: 543–551. - PubMed
-
- Yoshida H, Okabe Y, Kawane K, Fukuyama H, Nagata S (2005) Lethal anemia caused by interferon-beta produced in mouse embryos carrying undigested DNA. Nat Immunol 6: 49–56. - PubMed
-
- Leadbetter EA, Rifkin IR, Hohlbaum AM, Beaudette BC, Shlomchik MJ, et al. (2002) Chromatin-IgG complexes activate B cells by dual engagement of IgM and Toll-like receptors. Nature 416: 603–607. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

