Activation of Melatonin Signaling Promotes β-Cell Survival and Function
- PMID: 25695910
- PMCID: PMC4415205
- DOI: 10.1210/me.2014-1293
Activation of Melatonin Signaling Promotes β-Cell Survival and Function
Abstract
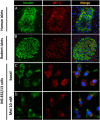
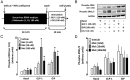
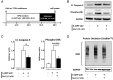
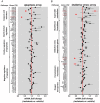
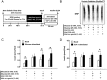
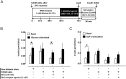
Type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) is characterized by pancreatic islet failure due to loss of β-cell secretory function and mass. Studies have identified a link between a variance in the gene encoding melatonin (MT) receptor 2, T2DM, and impaired insulin secretion. This genetic linkage raises the question whether MT signaling plays a role in regulation of β-cell function and survival in T2DM. To address this postulate, we used INS 832/13 cells to test whether activation of MT signaling attenuates proteotoxicity-induced β-cell apoptosis and through which molecular mechanism. We also used nondiabetic and T2DM human islets to test the potential of MT signaling to attenuate deleterious effects of glucotoxicity and T2DM on β-cell function. MT signaling in β-cells (with duration designed to mimic typical nightly exposure) significantly enhanced activation of the cAMP-dependent signal transduction pathway and attenuated proteotoxicity-induced β-cell apoptosis evidenced by reduced caspase-3 cleavage (∼40%), decreased activation of stress-activated protein kinase/Jun-amino-terminal kinase (∼50%) and diminished oxidative stress response. Activation of MT signaling in human islets was shown to restore glucose-stimulated insulin secretion in islets exposed to chronic hyperglycemia as well as in T2DM islets. Our data suggest that β-cell MT signaling is important for the regulation of β-cell survival and function and implies a preventative and therapeutic potential for preservation of β-cell mass and function in T2DM.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Fibroblast growth factor-21 improves pancreatic beta-cell function and survival by activation of extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2 and Akt signaling pathways.Diabetes. 2006 Sep;55(9):2470-8. doi: 10.2337/db05-1435. Diabetes. 2006. PMID: 16936195
-
Melatonin prevents pancreatic β-cell loss due to glucotoxicity: the relationship between oxidative stress and endoplasmic reticulum stress.J Pineal Res. 2014 Mar;56(2):143-53. doi: 10.1111/jpi.12106. Epub 2013 Nov 25. J Pineal Res. 2014. PMID: 24168371
-
MicroRNA-125b-5p improves pancreatic β-cell function through inhibiting JNK signaling pathway by targeting DACT1 in mice with type 2 diabetes mellitus.Life Sci. 2019 May 1;224:67-75. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2019.01.031. Epub 2019 Jan 23. Life Sci. 2019. PMID: 30684546
-
Melatonin, endocrine pancreas and diabetes.J Pineal Res. 2008 Jan;44(1):26-40. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-079X.2007.00519.x. J Pineal Res. 2008. PMID: 18078445 Review.
-
beta-cell failure in diabetes and preservation by clinical treatment.Endocr Rev. 2007 Apr;28(2):187-218. doi: 10.1210/10.1210/er.2006-0038. Epub 2007 Mar 12. Endocr Rev. 2007. PMID: 17353295 Review.
Cited by
-
Glucagon-like peptide-1: The missing link in the metabolic clock?J Diabetes Investig. 2016 Apr;7 Suppl 1(Suppl 1):70-5. doi: 10.1111/jdi.12477. Epub 2016 Mar 14. J Diabetes Investig. 2016. PMID: 27186359 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Melatonin receptors: molecular pharmacology and signalling in the context of system bias.Br J Pharmacol. 2018 Aug;175(16):3263-3280. doi: 10.1111/bph.13950. Epub 2017 Aug 17. Br J Pharmacol. 2018. PMID: 28707298 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Administration of Melatonin and Metformin Prevents Deleterious Effects of Circadian Disruption and Obesity in Male Rats.Endocrinology. 2016 Dec;157(12):4720-4731. doi: 10.1210/en.2016-1309. Epub 2016 Sep 21. Endocrinology. 2016. PMID: 27653034 Free PMC article.
-
The islet circadian clock: entrainment mechanisms, function and role in glucose homeostasis.Diabetes Obes Metab. 2015 Sep;17 Suppl 1(0 1):115-22. doi: 10.1111/dom.12523. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2015. PMID: 26332976 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Therapeutic potential of melatonin as a chronobiotic and cytoprotective agent in diabetes mellitus.J Diabetes Metab Disord. 2020 Jul 21;19(2):1797-1825. doi: 10.1007/s40200-020-00585-2. eCollection 2020 Dec. J Diabetes Metab Disord. 2020. PMID: 33520862 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Brunzell JD, Robertson RP, Lerner RL, et al. Relationships between fasting plasma glucose levels and insulin secretion during intravenous glucose tolerance tests. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1976;42:222–229. - PubMed
-
- Butler AE, Janson J, Bonner-Weir S, Ritzel R, Rizza RA, Butler PC. β-Cell deficit and increased β-cell apoptosis in humans with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes. 2003;52:102–110. - PubMed
-
- Marchetti P, Del Guerra S, Marselli L, et al. Pancreatic islets from type 2 diabetic patients have functional defects and increased apoptosis that are ameliorated by metformin. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2004;89:5535–5541. - PubMed
-
- Yoneda S, Uno S, Iwahashi H, et al. Predominance of β-cell neogenesis rather than replication in humans with an impaired glucose tolerance and newly diagnosed diabetes. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2013;98:2053–2061. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

