Dietary patterns in India and their association with obesity and central obesity
- PMID: 25697609
- PMCID: PMC4831640
- DOI: 10.1017/S1368980015000312
Dietary patterns in India and their association with obesity and central obesity
Abstract
Objective: Obesity is a growing problem in India, the dietary determinants of which have been studied using an 'individual food/nutrient' approach. Examining dietary patterns may provide more coherent findings, but few studies in developing countries have adopted this approach. The present study aimed to identify dietary patterns in an Indian population and assess their relationship with anthropometric risk factors.
Design: FFQ data from the cross-sectional sib-pair Indian Migration Study (IMS; n 7067) were used to identify dietary patterns using principal component analysis. Mixed-effects logistic regression was used to examine associations with obesity and central obesity.
Setting: The IMS was conducted at four factory locations across India: Lucknow, Nagpur, Hyderabad and Bangalore.
Subjects: The participants were rural-to-urban migrant and urban non-migrant factory workers, their rural and urban resident siblings, and their co-resident spouses.
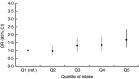
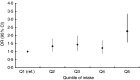
Results: Three dietary patterns were identified: 'cereals-savoury foods' (cooked grains, rice/rice-based dishes, snacks, condiments, soups, nuts), 'fruit-veg-sweets-snacks' (Western cereals, vegetables, fruit, fruit juices, cooked milk products, snacks, sugars, sweets) and 'animal-food' (red meat, poultry, fish/seafood, eggs). In adjusted analysis, positive graded associations were found between the 'animal-food' pattern and both anthropometric risk factors. Moderate intake of the 'cereals-savoury foods' pattern was associated with reduced odds of obesity and central obesity.
Conclusions: Distinct dietary patterns were identified in a large Indian sample, which were different from those identified in previous literature. A clear 'plant food-based/animal food-based pattern' dichotomy emerged, with the latter being associated with higher odds of anthropometric risk factors. Longitudinal studies are needed to further clarify this relationship in India.
Keywords: Central obesity; Dietary patterns; India; Indian Migration Study; Obesity.
Figures
References
-
- Finucane MM, Stevens GA, Cowan MJ et al.; Global Burden of Metabolic Risk Factors of Chronic Diseases Collaborating Group (Body Mass Index) (2011) National, regional, and global trends in body-mass index since 1980: Systematic analysis of health examination surveys and epidemiological studies with 960 country-years and 9.1 million participants. Lancet 377, 557–567. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Hu FB, Rimm E, Smith-Warner SA et al. (1999) Reproducibility and validity of dietary patterns assessed with a food-frequency questionnaire. Am J Clin Nutr 69, 243–249. - PubMed
-
- Millen BE, Quatromoni PA, Copenhafer DL et al. (2001) Validation of a dietary pattern approach for evaluating nutritional risk: the Framingham Nutrition Studies. J Am Diet Assoc 101, 187–194. - PubMed
-
- Hu FB (2008) Obesity Epidemiology. New York: Oxford University Press.
-
- Fung TT, Rimm EB, Spiegelman D et al. (2001) Association between dietary patterns and plasma biomarkers of obesity and cardiovascular disease risk. Am J Clin Nutr 73, 61–67. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

