Cigarette smoke exposure reveals a novel role for the MEK/ERK1/2 MAPK pathway in regulation of CFTR
- PMID: 25697727
- PMCID: PMC4398641
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbagen.2015.02.004
Cigarette smoke exposure reveals a novel role for the MEK/ERK1/2 MAPK pathway in regulation of CFTR
Abstract
Background: Cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator plays a key role in maintenance of lung fluid homeostasis. Cigarette smoke decreases CFTR expression in the lung but neither the mechanisms leading to CFTR loss, nor potential ways to prevent its loss have been identified to date.
Methods: The molecular mechanisms leading to down-regulation of CFTR by cigarette smoke were determined using pharmacologic inhibitors and silencing ribonucleic acids (RNAs).
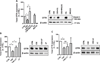
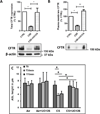
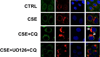
Results: Using human bronchial epithelial cells, here we show that cigarette smoke induces degradation of CFTR that is attenuated by lysosomal inhibitors, but not proteasome inhibitors. Cigarette smoke can activate multiple signaling pathways in airway epithelial cells, including the MEK/Erk1/2 MAPK (MEK: mitogen-activated protein kinase/ERK kinase Erk1/2: extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2 MAPK: Mitogen-activated protein kinase) pathway regulating cell survival. Interestingly, pharmacological inhibition of the MEK/Erk1/2 MAPK pathway prevented the loss of plasma membrane CFTR upon cigarette smoke exposure. Similarly, decreased expression of Erk1/2 using silencing RNAs prevented the suppression of CFTR protein by cigarette smoke. Conversely, specific inhibitors of the c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK) or p38 MAPK pathways had no effect on CFTR decrease after cigarette smoke exposure. In addition, inhibition of the MEK/Erk1/2 MAPK pathway prevented the reduction of the airway surface liquid observed upon cigarette smoke exposure of primary human airway epithelial cells. Finally, addition of the antioxidant N-acetylcysteine inhibited activation of Erk1/2 by cigarette smoke and precluded the cigarette smoke-induced decrease of CFTR.
Conclusions: These results show that the MEK/Erk1/2 MAPK pathway regulates plasma membrane CFTR in human airway cells.
General significance: The MEK/Erk1/2 MAPK pathway should be considered as a target for strategies to maintain/restore CFTR expression in the lung of smokers.
Keywords: Airway epithelial cell; CFTR; Cigarette smoke; MAPK pathway.
Copyright © 2015 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures
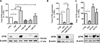
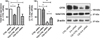
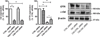

Similar articles
-
The role of MAPK and Nrf2 pathways in ketanserin-elicited attenuation of cigarette smoke-induced IL-8 production in human bronchial epithelial cells.Toxicol Sci. 2012 Feb;125(2):569-77. doi: 10.1093/toxsci/kfr305. Epub 2011 Nov 1. Toxicol Sci. 2012. PMID: 22048642
-
Cigarette smoke extract induces placental growth factor release from human bronchial epithelial cells via ROS/MAPK (ERK-1/2)/Egr-1 axis.Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2016 Dec 2;11:3031-3042. doi: 10.2147/COPD.S120849. eCollection 2016. Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2016. PMID: 27980400 Free PMC article.
-
Roflumilast partially reverses smoke-induced mucociliary dysfunction.Respir Res. 2015 Oct 31;16:135. doi: 10.1186/s12931-015-0294-3. Respir Res. 2015. PMID: 26521141 Free PMC article.
-
Cigarette Smoke-Induced Acquired Dysfunction of Cystic Fibrosis Transmembrane Conductance Regulator in the Pathogenesis of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2018 Apr 23;2018:6567578. doi: 10.1155/2018/6567578. eCollection 2018. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2018. PMID: 29849907 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Role of ERK1/2 in the Development of Diabetic Cardiomyopathy.Int J Mol Sci. 2016 Dec 8;17(12):2001. doi: 10.3390/ijms17122001. Int J Mol Sci. 2016. PMID: 27941647 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
DNA Methylation in Babies Born to Nonsmoking Mothers Exposed to Secondhand Smoke during Pregnancy: An Epigenome-Wide Association Study.Environ Health Perspect. 2021 May;129(5):57010. doi: 10.1289/EHP8099. Epub 2021 May 19. Environ Health Perspect. 2021. PMID: 34009014 Free PMC article.
-
Fibroblast growth factor 23 and Klotho contribute to airway inflammation.Eur Respir J. 2018 Jul 4;52(1):1800236. doi: 10.1183/13993003.00236-2018. Print 2018 Jul. Eur Respir J. 2018. PMID: 29748308 Free PMC article.
-
30-Min Exposure to Tobacco Smoke Influences Airway Ion Transport-An In Vitro Study.Curr Oncol. 2023 Jul 22;30(7):7007-7018. doi: 10.3390/curroncol30070508. Curr Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37504368 Free PMC article.
-
Roles of TGF-β signaling pathway in endoplasmic reticulum stress in endothelial cells stimulated with cigarette smoke extract.J Huazhong Univ Sci Technolog Med Sci. 2017 Oct;37(5):699-704. doi: 10.1007/s11596-017-1791-z. Epub 2017 Oct 20. J Huazhong Univ Sci Technolog Med Sci. 2017. PMID: 29058282
-
Role of Smad3 and p38 Signalling in Cigarette Smoke-induced CFTR and BK dysfunction in Primary Human Bronchial Airway Epithelial Cells.Sci Rep. 2017 Sep 5;7(1):10506. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-11038-x. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28874823 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Boucher RC. Evidence for airway surface dehydration as the initiating event in CF airway disease. Journal of internal medicine. 2007;261:5–16. - PubMed
-
- Boucher RC. New concepts of the pathogenesis of cystic fibrosis lung disease. The European respiratory journal. 2004;23:146–158. - PubMed
-
- Cantin AM, Hanrahan JW, Bilodeau G, Ellis L, Dupuis A, Liao J, Zielenski J, Durie P. Cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator function is suppressed in cigarette smokers. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2006;173:1139–1144. - PubMed
-
- Stanton CR, Thibodeau R, Lankowski A, Shaw JR, Hamilton JW, Stanton BA. Arsenic inhibits CFTR-mediated chloride secretion by killifish (Fundulus heteroclitus) opercular membrane. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2006;17:269–278. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

