Adaptation of a small-molecule hydrogen-bond donor catalyst to an enantioselective hetero-Diels-Alder reaction hypothesized for brevianamide biosynthesis
- PMID: 25697748
- PMCID: PMC4339957
- DOI: 10.1021/ol503626w
Adaptation of a small-molecule hydrogen-bond donor catalyst to an enantioselective hetero-Diels-Alder reaction hypothesized for brevianamide biosynthesis
Abstract
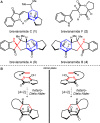
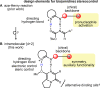
Chiral diamine-derived hydrogen-bond donors were evaluated for their ability to effect stereocontrol in an intramolecular hetero-Diels-Alder (HDA) reaction hypothesized in the biosynthesis of brevianamides A and B. Collectively, these results provide proof of principle that small-molecule hydrogen-bond catalysis, if even based on a hypothetical biosynthesis construct, holds significant potential within enantioselective natural product synthesis.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

