Biophysical methods for the characterization of PTEN/lipid bilayer interactions
- PMID: 25697761
- PMCID: PMC4388815
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ymeth.2015.02.004
Biophysical methods for the characterization of PTEN/lipid bilayer interactions
Abstract
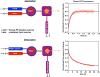
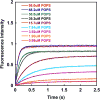
PTEN, a tumor suppressor protein that dephosphorylates phosphoinositides at the 3-position of the inositol ring, is a cytosolic protein that needs to associate with the plasma membrane or other subcellular membranes to exert its lipid phosphatase function. Upon membrane association PTEN interacts with at least three different lipid entities: An anionic lipid that is present in sufficiently high concentration to create a negative potential that allows PTEN to interact electrostatically with the membrane, phosphatidylinositol-4,5-bisphosphate, which interacts with PTEN's N-terminal end and the substrate, usually phosphatidylinositol-3,4,5-trisphosphate. Many parameters influence PTEN's interaction with the lipid bilayer, for example, the lateral organization of the lipids or the presence of other chemical species like cholesterol or other lipids. To investigate systematically the different steps of PTEN's complex binding mechanism and to explore its dynamic behavior in the membrane bound state, in vitro methods need to be employed that allow for a systematic variation of the experimental conditions. In this review we survey a variety of methods that can be used to assess PTEN lipid binding affinity, the dynamics of its membrane association as well as its dynamic behavior in the membrane bound state.
Keywords: Conformational change; PTEN; Peripheral membrane protein; Phosphatase; Single-particle tracking; Spectroscopy.
Copyright © 2015 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures



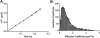
Similar articles
-
Membrane association of the PTEN tumor suppressor: electrostatic interaction with phosphatidylserine-containing bilayers and regulatory role of the C-terminal tail.J Struct Biol. 2012 Dec;180(3):394-408. doi: 10.1016/j.jsb.2012.10.003. Epub 2012 Oct 13. J Struct Biol. 2012. PMID: 23073177 Free PMC article.
-
A mutant form of PTEN linked to autism.Protein Sci. 2010 Oct;19(10):1948-56. doi: 10.1002/pro.483. Protein Sci. 2010. PMID: 20718038 Free PMC article.
-
Defining the membrane-associated state of the PTEN tumor suppressor protein.Biophys J. 2013 Feb 5;104(3):613-21. doi: 10.1016/j.bpj.2012.12.002. Biophys J. 2013. PMID: 23442912 Free PMC article.
-
Study of PTEN subcellular localization.Methods. 2015 May;77-78:92-103. doi: 10.1016/j.ymeth.2014.10.002. Epub 2014 Oct 13. Methods. 2015. PMID: 25312582 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Regulation of PTEN function as a PIP3 gatekeeper through membrane interaction.Cell Cycle. 2006 Jul;5(14):1523-7. doi: 10.4161/cc.5.14.3005. Epub 2006 Jul 17. Cell Cycle. 2006. PMID: 16861931 Review.
Cited by
-
Graph-Theoretic Analysis of Monomethyl Phosphate Clustering in Ionic Solutions.J Phys Chem B. 2018 Feb 1;122(4):1484-1494. doi: 10.1021/acs.jpcb.7b10730. Epub 2018 Jan 22. J Phys Chem B. 2018. PMID: 29293344 Free PMC article.
-
Kinetics of PTEN-mediated PI(3,4,5)P3 hydrolysis on solid supported membranes.PLoS One. 2018 Feb 15;13(2):e0192667. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0192667. eCollection 2018. PLoS One. 2018. PMID: 29447222 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of C2 Domains in Two Different Phosphatases: PTEN and SHIP2.Membranes (Basel). 2023 Apr 4;13(4):408. doi: 10.3390/membranes13040408. Membranes (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37103835 Free PMC article.
-
Multiple Inositol Polyphosphate Phosphatase Compartmentalization Separates Inositol Phosphate Metabolism from Inositol Lipid Signaling.Biomolecules. 2023 May 24;13(6):885. doi: 10.3390/biom13060885. Biomolecules. 2023. PMID: 37371464 Free PMC article.
-
Binding of Ca2+-independent C2 domains to lipid membranes: A multi-scale molecular dynamics study.Structure. 2021 Oct 7;29(10):1200-1213.e2. doi: 10.1016/j.str.2021.05.011. Epub 2021 Jun 2. Structure. 2021. PMID: 34081910 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

