A specific hypoactivation of right temporo-parietal junction/posterior superior temporal sulcus in response to socially awkward situations in autism
- PMID: 25698698
- PMCID: PMC4590532
- DOI: 10.1093/scan/nsv021
A specific hypoactivation of right temporo-parietal junction/posterior superior temporal sulcus in response to socially awkward situations in autism
Abstract
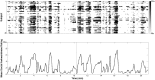
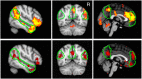
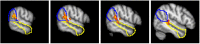
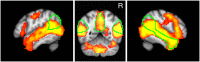
People with autism spectrum disorder (ASD) often have difficulty comprehending social situations in the complex, dynamic contexts encountered in the real world. To study the social brain under conditions which approximate naturalistic situations, we measured brain activity with FUNCTIONAL MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING: while participants watched a full-length episode of the sitcom The Office. Having quantified the degree of social awkwardness at each moment of the episode, as judged by an independent sample of controls, we found that both individuals with ASD and control participants showed reliable activation of several brain regions commonly associated with social perception and cognition (e.g. those comprising the 'mentalizing network') during the more awkward moments. However, individuals with ASD showed less activity than controls in a region near right temporo-parietal junction (RTPJ) extending into the posterior end of the right superior temporal sulcus (RSTS). Further analyses suggested that, despite the free-form nature of the experimental design, this group difference was specific to this RTPJ/RSTS area of the mentalizing network; other regions of interest showed similar activity across groups with respect to both location and magnitude. These findings add support to a body of evidence suggesting that RTPJ/RSTS plays a special role in social processes across modalities and may function atypically in individuals with ASD navigating the social world.
Keywords: autism; fMRI; mentalizing; right posterior superior temporal sulcus; right temporo-parietal junction; social cognition.
© The Author (2015). Published by Oxford University Press. For Permissions, please email: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Figures

References
-
- American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, 5th edn. Arlington, VA: American Psychiatric Publishing; 2013.
-
- Baron Cohen S, O’Riordan M, Stone V, Jones R, Plaisted K. Recognition of faux pas by normally developing children and children with Asperger syndrome or high-functioning autism. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders. 1999;29:407–18. - PubMed
-
- Berthoz S, Armony JL, Blair RJR, Dolan RJ. An fMRI study of intentional and unintentional (embarrassing) violations of social norms. Brain. 2002;125:1696–708. - PubMed
-
- Bidet-Caulet A, Voisin J, Bertrand O, Fonlupt P. Listening to a walking human activates the temporal biological motion area. NeuroImage. 2005;28:132–9. - PubMed
-
- Burnham KP, Anderson DR. Model Selection and Multi-Model Inference: A Practical Information-Theoretic Approach. New York: Springer; 2002.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

