Striatal D(2/3) Binding Potential Values in Drug-Naïve First-Episode Schizophrenia Patients Correlate With Treatment Outcome
- PMID: 25698711
- PMCID: PMC4535636
- DOI: 10.1093/schbul/sbu220
Striatal D(2/3) Binding Potential Values in Drug-Naïve First-Episode Schizophrenia Patients Correlate With Treatment Outcome
Abstract
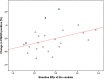
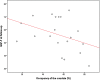
One of best validated findings in schizophrenia research is the association between blockade of dopamine D2 receptors and the effects of antipsychotics on positive psychotic symptoms. The aim of the present study was to examine correlations between baseline striatal D(2/3) receptor binding potential (BP(p)) values and treatment outcome in a cohort of antipsychotic-naïve first-episode schizophrenia patients. Additionally, we wished to investigate associations between striatal dopamine D(2/3) receptor blockade and alterations of negative symptoms as well as functioning and subjective well-being. Twenty-eight antipsychotic-naïve schizophrenia patients and 26 controls were included in the study. Single-photon emission computed tomography (SPECT) with [(123)I]iodobenzamide ([(123)I]-IBZM) was used to examine striatal D(2/3) receptor BP(p). Patients were examined before and after 6 weeks of treatment with the D(2/3) receptor antagonist amisulpride. There was a significant negative correlation between striatal D(2/3) receptor BP(p) at baseline and improvement of positive symptoms in the total group of patients. Comparing patients responding to treatment to nonresponders further showed significantly lower baseline BP(p) in the responders. At follow-up, the patients demonstrated a negative correlation between the blockade and functioning, whereas no associations between blockade and negative symptoms or subjective well-being were observed. The results show an association between striatal BP(p) of dopamine D(2/3) receptors in antipsychotic-naïve first-episode patients with schizophrenia and treatment response. Patients with a low BP(p) have a better treatment response than patients with a high BP(p). The results further suggest that functioning may decline at high levels of dopamine receptor blockade.
Keywords: SPECT; [123I]iodobenzamide; amisulpride; occupancy; subjective well-being.
© The Author 2015. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the Maryland Psychiatric Research Center.
Figures
Similar articles
-
D2 receptor occupancy during high- and low-dose therapy with the atypical antipsychotic amisulpride: a 123I-iodobenzamide SPECT study.J Nucl Med. 2005 Jun;46(6):1028-33. J Nucl Med. 2005. PMID: 15937316
-
Is regionally selective D2/D3 dopamine occupancy sufficient for atypical antipsychotic effect? an in vivo quantitative [123I]epidepride SPET study of amisulpride-treated patients.Am J Psychiatry. 2003 Aug;160(8):1413-20. doi: 10.1176/appi.ajp.160.8.1413. Am J Psychiatry. 2003. PMID: 12900302
-
Frontal fasciculi and psychotic symptoms in antipsychotic-naive patients with schizophrenia before and after 6 weeks of selective dopamine D2/3 receptor blockade.J Psychiatry Neurosci. 2016 Mar;41(2):133-41. doi: 10.1503/jpn.150030. J Psychiatry Neurosci. 2016. PMID: 26599135 Free PMC article.
-
Estimating dopamine D₂ receptor occupancy for doses of 8 antipsychotics: a meta-analysis.J Clin Psychopharmacol. 2013 Oct;33(5):675-81. doi: 10.1097/JCP.0b013e3182983ffa. J Clin Psychopharmacol. 2013. PMID: 23948784 Review.
-
What proportion of striatal D2 receptors are occupied by endogenous dopamine at baseline? A meta-analysis with implications for understanding antipsychotic occupancy.Neuropharmacology. 2020 Feb;163:107591. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2019.03.034. Epub 2019 Mar 30. Neuropharmacology. 2020. PMID: 30940535
Cited by
-
Treatment response after 6 and 26 weeks is related to baseline glutamate and GABA levels in antipsychotic-naïve patients with psychosis.Psychol Med. 2020 Oct;50(13):2182-2193. doi: 10.1017/S0033291719002277. Epub 2019 Sep 16. Psychol Med. 2020. PMID: 31524118 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical Course, Neurobiology and Therapeutic Approaches to Treatment Resistant Schizophrenia. Toward an Integrated View.Front Psychiatry. 2019 Sep 3;10:601. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2019.00601. eCollection 2019. Front Psychiatry. 2019. PMID: 31551822 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A brain imaging study of dopamine receptor D2 availability in cannabis dependent users after recovery from cannabis-induced psychosis.Front Psychiatry. 2023 Oct 27;14:1230760. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2023.1230760. eCollection 2023. Front Psychiatry. 2023. PMID: 37965367 Free PMC article.
-
Amotivation is associated with smaller ventral striatum volumes in older patients with schizophrenia.Int J Geriatr Psychiatry. 2018 Mar;33(3):523-530. doi: 10.1002/gps.4818. Epub 2017 Nov 7. Int J Geriatr Psychiatry. 2018. PMID: 29110353 Free PMC article.
-
Functional Connectivity Between Auditory and Medial Temporal Lobe Networks in Antipsychotic-Naïve Patients With First-Episode Schizophrenia Predicts the Effects of Dopamine Antagonism on Auditory Verbal Hallucinations.Biol Psychiatry Glob Open Sci. 2023 Jul 6;4(1):308-316. doi: 10.1016/j.bpsgos.2023.06.003. eCollection 2024 Jan. Biol Psychiatry Glob Open Sci. 2023. PMID: 38298804 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hietala J, Syvälahti E, Vuorio K, et al. Presynaptic dopamine function in striatum of neuroleptic-naive schizophrenic patients. Lancet. 1995;346:1130–1131. - PubMed
-
- Abi-Dargham A, Gil R, Krystal J, et al. Increased striatal dopamine transmission in schizophrenia: confirmation in a second cohort. Am J Psychiatry. 1998;155:761–767. - PubMed
-
- Laruelle M, Abi-Dargham A, Gil R, Kegeles L, Innis R. Increased dopamine transmission in schizophrenia: relationship to illness phases. Biol Psychiatry. 1999;46:56–72. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

