Reciprocal interareal connections to corticospinal neurons in mouse M1 and S2
- PMID: 25698734
- PMCID: PMC4331623
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4287-14.2015
Reciprocal interareal connections to corticospinal neurons in mouse M1 and S2
Abstract
Primary motor (M1) and secondary somatosensory (S2) cortices, although anatomically and functionally distinct, share an intriguing cellular component: corticospinal neurons (CSP) in layer 5B. Here, we investigated the long-range circuits of CSPs in mouse forelimb-M1 and S2. We found that interareal projections (S2 → M1 and M1 → S2) monosynaptically excited pyramidal neurons across multiple layers, including CSPs. Area-specific differences were observed in the relative strengths of inputs to subsets of CSPs and other cell types, but the general patterns were similar. Furthermore, subcellular mapping of the dendritic distributions of these corticocortical excitatory synapses onto CSPs in both areas also showed similar patterns. Because layer 5B is particularly thick in M1, but not S2, we studied M1-CSPs at different cortical depths, quantifying their dendritic morphology and mapping inputs from additional cortical (M2, contralateral M1, and local layer 2/3) and thalamic (VL nucleus) sources. These results indicated that CSPs exhibit area-specific modifications on an otherwise conserved synaptic organization, and that different afferents innervate M1-CSP dendritic domains in a source-specific manner. In the cervical spinal cord, CSP axons from S2 and M1 partly converged on middle layers, but S2-CSP axons extended further dorsally, and M1-CSP axons ventrally. Thus, our findings identify many shared features in the circuits of M1 and S2 and show that these areas communicate via mutual projections that give each area monosynaptic access to the other area's CSPs. These interareally yoked CSP circuits may enable M1 and S2 to operate in a coordinated yet differentiated manner in the service of sensorimotor integration.
Keywords: corticocortical; corticospinal; motor; somatosensory; subcellular.
Copyright © 2015 the authors 0270-6474/15/352959-16$15.00/0.
Figures

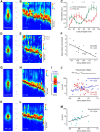
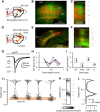

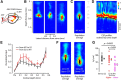
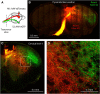
Similar articles
-
Anterolateral Motor Cortex Connects with a Medial Subdivision of Ventromedial Thalamus through Cell Type-Specific Circuits, Forming an Excitatory Thalamo-Cortico-Thalamic Loop via Layer 1 Apical Tuft Dendrites of Layer 5B Pyramidal Tract Type Neurons.J Neurosci. 2018 Oct 10;38(41):8787-8797. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1333-18.2018. Epub 2018 Aug 24. J Neurosci. 2018. PMID: 30143573 Free PMC article.
-
A Corticocortical Circuit Directly Links Retrosplenial Cortex to M2 in the Mouse.J Neurosci. 2016 Sep 7;36(36):9365-74. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1099-16.2016. J Neurosci. 2016. PMID: 27605612 Free PMC article.
-
Organization of cortical and thalamic input to pyramidal neurons in mouse motor cortex.J Neurosci. 2013 Jan 9;33(2):748-60. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4338-12.2013. J Neurosci. 2013. PMID: 23303952 Free PMC article.
-
Functional differences in corticospinal projections from macaque primary motor cortex and supplementary motor area.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2002;508:425-34. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4615-0713-0_48. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2002. PMID: 12171139 Review.
-
Local connections of excitatory neurons in motor-associated cortical areas of the rat.Front Neural Circuits. 2013 May 28;7:75. doi: 10.3389/fncir.2013.00075. eCollection 2013. Front Neural Circuits. 2013. PMID: 23754982 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Sensory and decision-related activity propagate in a cortical feedback loop during touch perception.Nat Neurosci. 2016 Sep;19(9):1243-9. doi: 10.1038/nn.4356. Epub 2016 Jul 20. Nat Neurosci. 2016. PMID: 27437910 Free PMC article.
-
Axonal connections between S1 barrel, M1, and S2 cortex in the newborn mouse.Front Neuroanat. 2023 Jan 25;17:1105998. doi: 10.3389/fnana.2023.1105998. eCollection 2023. Front Neuroanat. 2023. PMID: 36760662 Free PMC article.
-
Topographical and cell type-specific connectivity of rostral and caudal forelimb corticospinal neuron populations.Cell Rep. 2024 Apr 23;43(4):113993. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2024.113993. Epub 2024 Mar 27. Cell Rep. 2024. PMID: 38551963 Free PMC article.
-
Structural dynamics and stability of corticocortical and thalamocortical axon terminals during motor learning.PLoS One. 2020 Jun 19;15(6):e0234930. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0234930. eCollection 2020. PLoS One. 2020. PMID: 32559228 Free PMC article.
-
Large-scale all-optical dissection of motor cortex connectivity shows a segregated organization of mouse forelimb representations.Cell Rep. 2022 Nov 8;41(6):111627. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2022.111627. Cell Rep. 2022. PMID: 36351410 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Burton H. Second somatosensory cortex and related areas. In: Jones EG, Peters A, editors. Cerebral cortex: sensory-motor areas and aspects of cortical connectivity. New York: Plenum; 1986. pp. 31–98.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
