Pannexin2 oligomers localize in the membranes of endosomal vesicles in mammalian cells while Pannexin1 channels traffic to the plasma membrane
- PMID: 25698922
- PMCID: PMC4313697
- DOI: 10.3389/fncel.2014.00468
Pannexin2 oligomers localize in the membranes of endosomal vesicles in mammalian cells while Pannexin1 channels traffic to the plasma membrane
Abstract
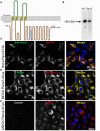
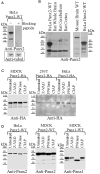
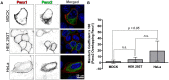
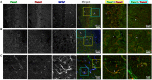
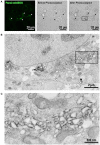
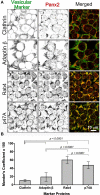
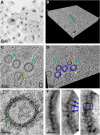
Pannexin2 (Panx2) is the largest of three members of the pannexin proteins. Pannexins are topologically related to connexins and innexins, but serve different functional roles than forming gap junctions. We previously showed that pannexins form oligomeric channels but unlike connexins and innexins, they form only single membrane channels. High levels of Panx2 mRNA and protein in the Central Nervous System (CNS) have been documented. Whereas Pannexin1 (Panx1) is fairly ubiquitous and Pannexin3 (Panx3) is found in skin and connective tissue, both are fully glycosylated, traffic to the plasma membrane and have functions correlated with extracellular ATP release. Here, we describe trafficking and subcellular localizations of exogenous Panx2 and Panx1 protein expression in MDCK, HeLa, and HEK 293T cells as well as endogenous Panx1 and Panx2 patterns in the CNS. Panx2 was found in intracellular localizations, was partially N-glycosylated, and localizations were non-overlapping with Panx1. Confocal images of hippocampal sections immunolabeled for the astrocytic protein GFAP, Panx1 and Panx2 demonstrated that the two isoforms, Panx1 and Panx2, localized at different subcellular compartments in both astrocytes and neurons. Using recombinant fusions of Panx2 with appended genetic tags developed for correlated light and electron microscopy and then expressed in different cell lines, we determined that Panx2 is localized in the membrane of intracellular vesicles and not in the endoplasmic reticulum as initially indicated by calnexin colocalization experiments. Dual immunofluorescence imaging with protein markers for specific vesicle compartments showed that Panx2 vesicles are early endosomal in origin. In electron tomographic volumes, cross-sections of these vesicles displayed fine structural details and close proximity to actin filaments. Thus, pannexins expressed at different subcellular compartments likely exert distinct functional roles, particularly in the nervous system.
Keywords: ATP signaling; connexin; correlated light and electron microscopy; electron tomography; intercellular communication; miniSOG; pannexin channels; tetracysteine tag.
Figures
References
-
- Boassa D., Berlanga M. L., Yang M. A., Terada M., Hu J., Bushong E. A., et al. (2013). Mapping the subcellular distribution of alpha-synuclein in neurons using genetically encoded probes for correlated light and electron microscopy: implications for Parkinson's disease pathogenesis. J. Neurosci. 33, 2605–2615. 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2898-12.2013 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

