Enhancing multiple object tracking performance with noninvasive brain stimulation: a causal role for the anterior intraparietal sulcus
- PMID: 25698943
- PMCID: PMC4318277
- DOI: 10.3389/fnsys.2015.00003
Enhancing multiple object tracking performance with noninvasive brain stimulation: a causal role for the anterior intraparietal sulcus
Abstract
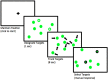
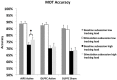
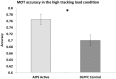
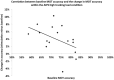
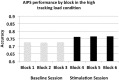
Multiple object tracking (MOT) is a complex task recruiting a distributed network of brain regions. There are also marked individual differences in MOT performance. A positive causal relationship between the anterior intraparietal sulcus (AIPS), an integral region in the MOT attention network and inter-individual variation in MOT performance has not been previously established. The present study used transcranial direct current stimulation (tDCS), a form of non-invasive brain stimulation, in order to examine such a causal link. Active anodal stimulation was applied to the right AIPS and the left dorsolateral prefrontal cortex (DLPFC) (and sham stimulation), an area associated with working memory (but not MOT) while participants completed a MOT task. Stimulation to the right AIPS significantly improved MOT accuracy more than the other two conditions. The results confirm a causal role of the AIPS in the MOT task and illustrate that tDCS has the ability to improve MOT performance.
Keywords: anterior intraparietal sulcus; brain stimulation; multiple object tracking; spatial attention; tDCS.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Modulating the interference effect on spatial working memory by applying transcranial direct current stimulation over the right dorsolateral prefrontal cortex.Brain Cogn. 2014 Nov;91:87-94. doi: 10.1016/j.bandc.2014.09.002. Epub 2014 Sep 29. Brain Cogn. 2014. PMID: 25265321
-
Effects of High-Definition Transcranial Direct Current Stimulation (HD-tDCS) of the Intraparietal Sulcus and Dorsolateral Prefrontal Cortex on Working Memory and Divided Attention.Front Integr Neurosci. 2019 Jan 8;12:64. doi: 10.3389/fnint.2018.00064. eCollection 2018. Front Integr Neurosci. 2019. PMID: 30670954 Free PMC article.
-
Balanced bifrontal transcranial direct current stimulation enhances working memory in adults with high-functioning autism: a sham-controlled crossover study.Mol Autism. 2017 Jul 28;8:40. doi: 10.1186/s13229-017-0152-x. eCollection 2017. Mol Autism. 2017. PMID: 28775825 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Transcranial Direct Current Stimulation (tDCS) over the Intraparietal Sulcus Does Not Influence Working Memory Performance.Psychol Belg. 2021 Jul 9;61(1):200-211. doi: 10.5334/pb.534. eCollection 2021. Psychol Belg. 2021. PMID: 34277028 Free PMC article.
-
Eye Behavior During Multiple Object Tracking and Multiple Identity Tracking.Vision (Basel). 2019 Jul 31;3(3):37. doi: 10.3390/vision3030037. Vision (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31735838 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Inter-Individual Variability in tDCS Effects: A Narrative Review on the Contribution of Stable, Variable, and Contextual Factors.Brain Sci. 2022 Apr 20;12(5):522. doi: 10.3390/brainsci12050522. Brain Sci. 2022. PMID: 35624908 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Neurotechnologies for Human Cognitive Augmentation: Current State of the Art and Future Prospects.Front Hum Neurosci. 2019 Jan 31;13:13. doi: 10.3389/fnhum.2019.00013. eCollection 2019. Front Hum Neurosci. 2019. PMID: 30766483 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cholinergic Potentiation Improves Perceptual-Cognitive Training of Healthy Young Adults in Three Dimensional Multiple Object Tracking.Front Hum Neurosci. 2017 Mar 21;11:128. doi: 10.3389/fnhum.2017.00128. eCollection 2017. Front Hum Neurosci. 2017. PMID: 28377707 Free PMC article.
-
Working memory capacity differentially influences responses to tDCS and HD-tDCS in a retro-cue task.Neurosci Lett. 2016 Aug 26;629:105-109. doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2016.06.056. Epub 2016 Jun 28. Neurosci Lett. 2016. PMID: 27369325 Free PMC article.
-
The neuropsychological profile of professional action video game players.PeerJ. 2020 Nov 17;8:e10211. doi: 10.7717/peerj.10211. eCollection 2020. PeerJ. 2020. PMID: 33240605 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Andrews S. C., Hoy K. E., Enticott P. G., Daskalakis Z. J., Fitzgerald P. B. (2011). Improving working memory: the effect of combining cognitive activity and anodal transcranial direct current stimulation to the left dorsolateral prefrontal cortex. Brain Stimul. 4, 84–89. 10.1016/j.brs.2010.06.004 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

