Fornix White Matter is Correlated with Resting-State Functional Connectivity of the Thalamus and Hippocampus in Healthy Aging but Not in Mild Cognitive Impairment - A Preliminary Study
- PMID: 25698967
- PMCID: PMC4318417
- DOI: 10.3389/fnagi.2015.00010
Fornix White Matter is Correlated with Resting-State Functional Connectivity of the Thalamus and Hippocampus in Healthy Aging but Not in Mild Cognitive Impairment - A Preliminary Study
Abstract
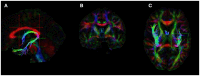
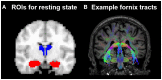
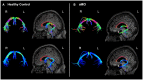
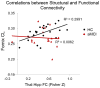
In this study, we wished to examine the relationship between the structural connectivity of the fornix, a white matter (WM) tract in the limbic system, which is affected in amnestic mild cognitive impairment (aMCI) and Alzheimer's disease, and the resting-state functional connectivity (FC) of two key related subcortical structures, the thalamus, and hippocampus. Twenty-two older healthy controls (HC) and 18 older adults with aMCI underwent multi-modal MRI scanning. The fornix was reconstructed using constrained-spherical deconvolution-based tractography. The FC between the thalamus and hippocampus was calculated using a region-of-interest approach from which the mean time series were exacted and correlated. Diffusion tensor imaging measures of the WM microstructure of the fornix were correlated against the Fisher Z correlation values from the FC analysis. There was no difference between the groups in the fornix WM measures, nor in the resting-state FC of the thalamus and hippocampus. We did however find that the relationship between functional and structural connectivity differed significantly between the groups. In the HCs, there was a significant positive association between linear diffusion (CL) in the fornix and the FC of the thalamus and hippocampus, however, there was no relationship between these measures in the aMCI group. These preliminary findings suggest that in aMCI, the relationship between the functional and structural connectivity of regions of the limbic system may be significantly altered compared to healthy ageing. The combined use of diffusion weighted imaging and functional MRI may advance our understanding of neural network changes in aMCI, and elucidate subtle changes in the relationship between structural and functional brain networks.
Keywords: diffusion MRI; fornix; functional connectivity; hippocampus; mild cognitive impairment (MCI); thalamus; tractography.
Figures
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

