Analysis of the Bovine Monocyte-Derived Macrophage Response to Mycobacterium avium Subspecies Paratuberculosis Infection Using RNA-seq
- PMID: 25699042
- PMCID: PMC4316787
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2015.00023
Analysis of the Bovine Monocyte-Derived Macrophage Response to Mycobacterium avium Subspecies Paratuberculosis Infection Using RNA-seq
Abstract
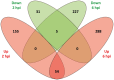
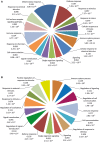
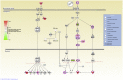
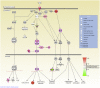
Johne's disease, caused by infection with Mycobacterium avium subsp. paratuberculosis, (MAP), is a chronic intestinal disease of ruminants with serious economic consequences for cattle production in the United States and elsewhere. During infection, MAP bacilli are phagocytosed and subvert host macrophage processes, resulting in subclinical infections that can lead to immunopathology and dissemination of disease. Analysis of the host macrophage transcriptome during infection can therefore shed light on the molecular mechanisms and host-pathogen interplay associated with Johne's disease. Here, we describe results of an in vitro study of the bovine monocyte-derived macrophage (MDM) transcriptome response during MAP infection using RNA-seq. MDM were obtained from seven age- and sex-matched Holstein-Friesian cattle and were infected with MAP across a 6-h infection time course with non-infected controls. We observed 245 and 574 differentially expressed (DE) genes in MAP-infected versus non-infected control samples (adjusted P value ≤0.05) at 2 and 6 h post-infection, respectively. Functional analyses of these DE genes, including biological pathway enrichment, highlighted potential functional roles for genes that have not been previously described in the host response to infection with MAP bacilli. In addition, differential expression of pro- and anti-inflammatory cytokine genes, such as those associated with the IL-10 signaling pathway, and other immune-related genes that encode proteins involved in the bovine macrophage response to MAP infection emphasize the balance between protective host immunity and bacilli survival and proliferation. Systematic comparisons of RNA-seq gene expression results with Affymetrix(®) microarray data generated from the same experimental samples also demonstrated that RNA-seq represents a superior technology for studying host transcriptional responses to intracellular infection.
Keywords: Johne’s disease; Mycobacterium avium subspecies paratuberculosis; RNA-sequencing; cattle; immune response; macrophage; microarray; transcriptome.
Figures
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

