Pharmacologic rationale, efficacy and safety of the fixed-dose co-formulation of indacaterol and glycopyrronium
- PMID: 25699181
- PMCID: PMC4333835
- DOI: 10.1186/2049-6958-9-64
Pharmacologic rationale, efficacy and safety of the fixed-dose co-formulation of indacaterol and glycopyrronium
Abstract
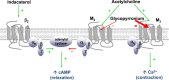
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is a widespread respiratory disorder, usually characterized by progressive and poorly reversible airflow limitation. Inhaled long-acting bronchodilators, namely LABA (long-acting β2-adrenergic agonists) and LAMA (long-acting muscarinic receptor antagonists) are the mainstay of COPD treatment. Because the symptoms of many patients with COPD do not satisfactorily improve by using a single, either LABA or LAMA bronchodilator, the synergism of action resulting from the combination of the different bronchodilating mechanisms activated by LABA and LAMA, respectively, can significantly contribute to a better disease control. Based on these clinical and pharmacological considerations, several LABA/LAMA fixed-dose combinations have been developed and experimentally evaluated. Within such a context, the drug co-formulation containing indacaterol and glycopyrronium is probably the LABA/LAMA association which has been most extensively studied during the last few years.
Keywords: Co-formulation; Dual bronchodilation; Glycopyrronium; Indacaterol; LABA; LAMA; QVA149; Synergism.
Figures
References
-
- Vestbo J, Hurd SS, Agusti AG, Jones PW, Vogelmeier C, Anzueto A, Barnes PJ, Fabbri LM, Martinez FJ, Nishimura M, Stockley RA, Sin DD, Rodriguez-Roisin R. Global strategy for the diagnosis, management, and prevention of chronic obstructive lung disease: GOLD executive summary. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2013;187:347–365. doi: 10.1164/rccm.201204-0596PP. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

