BRCA1 recruitment to transcriptional pause sites is required for R-loop-driven DNA damage repair
- PMID: 25699710
- PMCID: PMC4351672
- DOI: 10.1016/j.molcel.2015.01.011
BRCA1 recruitment to transcriptional pause sites is required for R-loop-driven DNA damage repair
Abstract
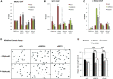
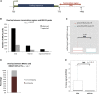
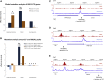
The mechanisms contributing to transcription-associated genomic instability are both complex and incompletely understood. Although R-loops are normal transcriptional intermediates, they are also associated with genomic instability. Here, we show that BRCA1 is recruited to R-loops that form normally over a subset of transcription termination regions. There it mediates the recruitment of a specific, physiological binding partner, senataxin (SETX). Disruption of this complex led to R-loop-driven DNA damage at those loci as reflected by adjacent γ-H2AX accumulation and ssDNA breaks within the untranscribed strand of relevant R-loop structures. Genome-wide analysis revealed widespread BRCA1 binding enrichment at R-loop-rich termination regions (TRs) of actively transcribed genes. Strikingly, within some of these genes in BRCA1 null breast tumors, there are specific insertion/deletion mutations located close to R-loop-mediated BRCA1 binding sites within TRs. Thus, BRCA1/SETX complexes support a DNA repair mechanism that addresses R-loop-based DNA damage at transcriptional pause sites.
Copyright © 2015 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Aguilera A., García-Muse T. R loops: from transcription byproducts to threats to genome stability. Mol. Cell. 2012;46:115–124. - PubMed
-
- Alexandrov L.B., Nik-Zainal S., Wedge D.C., Aparicio S.A.J.R., Behjati S., Biankin A.V., Bignell G.R., Bolli N., Borg A., Børresen-Dale A.-L., Australian Pancreatic Cancer Genome Initiative. ICGC Breast Cancer Consortium. ICGC MMML-Seq Consortium. ICGC PedBrain Signatures of mutational processes in human cancer. Nature. 2013;500:415–421. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Anderson S.F., Schlegel B.P., Nakajima T., Wolpin E.S., Parvin J.D. BRCA1 protein is linked to the RNA polymerase II holoenzyme complex via RNA helicase A. Nat. Genet. 1998;19:254–256. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

