Prehypertension and the risk of coronary heart disease in Asian and Western populations: a meta-analysis
- PMID: 25699996
- PMCID: PMC4345875
- DOI: 10.1161/JAHA.114.001519
Prehypertension and the risk of coronary heart disease in Asian and Western populations: a meta-analysis
Abstract
Background: The results of studies on the association between prehypertension (blood pressure 120 to 139/80 to 89 mm Hg) and coronary heart disease (CHD) remain controversial. Furthermore, it is unclear whether prehypertension affects the risk of CHD in Asian and Western populations differently. This meta-analysis evaluated the risk of CHD associated with prehypertension and its different subgroups.
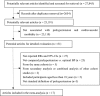
Methods and results: The PubMed and Embase databases were searched for prospective cohort studies with data on prehypertension and the risk of CHD. Studies were included if they reported multivariate-adjusted relative risks (RRs) with 95% CIs of CHD from prehypertension. A total of 591 664 participants from 17 prospective cohort studies were included. Prehypertension increased the risk of CHD (RR 1.43, 95% CI 1.26 to 1.63, P<0.001) compared with optimal blood pressure (<120/80 mm Hg). The risk of CHD was higher in Western than in Asian participants (Western: RR 1.70, 95% CI 1.49 to 1.94; Asian: RR 1.25, 95% CI 1.12 to 1.38; ratio of RRs 1.36, 95% CI 1.15 to 1.61). The population-attributable risk indicated that 8.4% of CHD in Asian participants was attributed to prehypertension, whereas this proportion was 24.1% in Western participants.
Conclusions: Prehypertension, even at the low range, is associated with an increased risk of CHD. This risk is more pronounced in Western than in Asian populations. These results supported the heterogeneity of target-organ damage caused by prehypertension and hypertension among different ethnicities and underscore the importance of prevention of CHD in Western patients with prehypertension.
Keywords: cardiovascular disease; coronary heart disease; prehypertension; risk.
© 2015 The Authors. Published on behalf of the American Heart Association, Inc., by Wiley Blackwell.
Figures


Comment in
-
Is 2015 the primetime year for prehypertension? Prehypertension: a cardiovascular risk factor or simply a risk marker?J Am Heart Assoc. 2015 Feb 19;4(2):e001792. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.115.001792. J Am Heart Assoc. 2015. PMID: 25699997 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Chobanian AV, Bakris GL, Black HR, Cushman WC, Green LA, Izzo JJ, Jones DW, Materson BJ, Oparil S, Wright JJ, Roccella EJ. The Seventh Report of the Joint National Committee on Prevention, Detection, Evaluation, and Treatment of High Blood Pressure: the JNC 7 report. JAMA. 2003; 289:2560-2572. - PubMed
-
- Huang Y, Cai X, Li Y, Su L, Mai W, Wang S, Hu Y, Wu Y, Xu D. Prehypertension and the risk of stroke: a meta‐analysis. Neurology. 2014; 82:1153-1161. - PubMed
-
- Qureshi AI, Suri MF, Kirmani JF, Divani AA, Mohammad Y. Is prehypertension a risk factor for cardiovascular diseases? Stroke. 2005; 36:1859-1863. - PubMed
-
- Lee ET, Howard BV, Wang W, Welty TK, Galloway JM, Best LG, Fabsitz RR, Zhang Y, Yeh J, Devereux RB. Prediction of coronary heart disease in a population with high prevalence of diabetes and albuminuria: the Strong Heart Study. Circulation. 2006; 113:2897-2905. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

