A novel cortical thickness estimation method based on volumetric Laplace-Beltrami operator and heat kernel
- PMID: 25700360
- PMCID: PMC4405465
- DOI: 10.1016/j.media.2015.01.005
A novel cortical thickness estimation method based on volumetric Laplace-Beltrami operator and heat kernel
Abstract
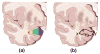
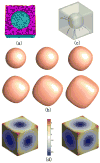
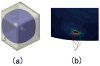
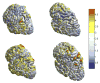
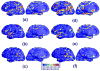
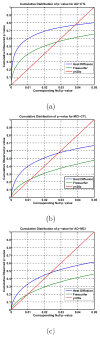
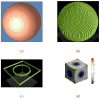
Cortical thickness estimation in magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is an important technique for research on brain development and neurodegenerative diseases. This paper presents a heat kernel based cortical thickness estimation algorithm, which is driven by the graph spectrum and the heat kernel theory, to capture the gray matter geometry information from the in vivo brain magnetic resonance (MR) images. First, we construct a tetrahedral mesh that matches the MR images and reflects the inherent geometric characteristics. Second, the harmonic field is computed by the volumetric Laplace-Beltrami operator and the direction of the steamline is obtained by tracing the maximum heat transfer probability based on the heat kernel diffusion. Thereby we can calculate the cortical thickness information between the point on the pial and white matter surfaces. The new method relies on intrinsic brain geometry structure and the computation is robust and accurate. To validate our algorithm, we apply it to study the thickness differences associated with Alzheimer's disease (AD) and mild cognitive impairment (MCI) on the Alzheimer's Disease Neuroimaging Initiative (ADNI) dataset. Our preliminary experimental results on 151 subjects (51 AD, 45 MCI, 55 controls) show that the new algorithm may successfully detect statistically significant difference among patients of AD, MCI and healthy control subjects. Our computational framework is efficient and very general. It has the potential to be used for thickness estimation on any biological structures with clearly defined inner and outer surfaces.
Keywords: Cortical thickness; False discovery rate; Heat kernel; Spectral analysis; Tetrahedral mesh.
Copyright © 2015 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures
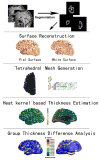

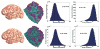
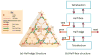
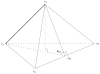




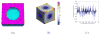
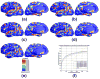
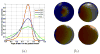
References
-
- Alzheimer’s Association. Alzheimer’s disease facts and figures. Alzheimer’s Association; 2012. http://www.alz.org. - PubMed
-
- Benjamini Y, Hochberg Y. Controlling the False Discovery Rate: A Practical and Powerful Approach to Multiple Testing. Journal of the Royal Statistical Society Series B (Methodological) 1995;57:289–300.
-
- Berg L. Clinical Dementia Rating (CDR) Psychopharmacol Bull. 1988;24:637–639. - PubMed
-
- Braak H, Braak E. Neuropathological stageing of Alzheimer-related changes. Acta Neuropathol. 1991;82:239–259. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

