Kinase dynamics. Using ancient protein kinases to unravel a modern cancer drug's mechanism
- PMID: 25700521
- PMCID: PMC4405104
- DOI: 10.1126/science.aaa1823
Kinase dynamics. Using ancient protein kinases to unravel a modern cancer drug's mechanism
Abstract
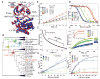
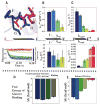
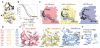
Macromolecular function is rooted in energy landscapes, where sequence determines not a single structure but an ensemble of conformations. Hence, evolution modifies a protein's function by altering its energy landscape. Here, we recreate the evolutionary pathway between two modern human oncogenes, Src and Abl, by reconstructing their common ancestors. Our evolutionary reconstruction combined with x-ray structures of the common ancestor and pre-steady-state kinetics reveals a detailed atomistic mechanism for selectivity of the successful cancer drug Gleevec. Gleevec affinity is gained during the evolutionary trajectory toward Abl and lost toward Src, primarily by shifting an induced-fit equilibrium that is also disrupted in the clinical T315I resistance mutation. This work reveals the mechanism of Gleevec specificity while offering insights into how energy landscapes evolve.
Copyright © 2015, American Association for the Advancement of Science.
Figures

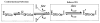
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

