Proteoglycan form and function: A comprehensive nomenclature of proteoglycans
- PMID: 25701227
- PMCID: PMC4859157
- DOI: 10.1016/j.matbio.2015.02.003
Proteoglycan form and function: A comprehensive nomenclature of proteoglycans
Abstract
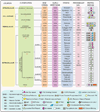
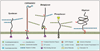
We provide a comprehensive classification of the proteoglycan gene families and respective protein cores. This updated nomenclature is based on three criteria: Cellular and subcellular location, overall gene/protein homology, and the utilization of specific protein modules within their respective protein cores. These three signatures were utilized to design four major classes of proteoglycans with distinct forms and functions: the intracellular, cell-surface, pericellular and extracellular proteoglycans. The proposed nomenclature encompasses forty-three distinct proteoglycan-encoding genes and many alternatively-spliced variants. The biological functions of these four proteoglycan families are critically assessed in development, cancer and angiogenesis, and in various acquired and genetic diseases where their expression is aberrant.
Keywords: Angiogenesis; Cancer growth; Glycosaminoglycan; Growth factor modulation; Proteoglycan.
Copyright © 2015.
Figures




References
-
- Iozzo RV, Murdoch AD. Proteoglycans of the extracellular environment: clues from the gene and protein side offer novel perspectives in molecular diversity and function. FASEB J. 1996;10:598–614. - PubMed
-
- Iozzo RV. Matrix proteoglycans: from molecular design to cellular function. Annu Rev Biochem. 1998;67:609–652. - PubMed
-
- Le BV, Kim H, Choi J, Kim J-H, Hahn M-J, Lee C, et al. Crystal structure of the LG3 domain of endorepellin, an angiogenesis inhibitor. J Mol Biol. 2011;414:231–242. - PubMed
-
- Couchman JR. Transmembrane signaling proteoglycans. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 2010;26:89–114. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

