Mechanical stress and network structure drive protein dynamics during cytokinesis
- PMID: 25702575
- PMCID: PMC4348339
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cub.2015.01.025
Mechanical stress and network structure drive protein dynamics during cytokinesis
Abstract
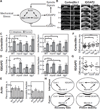
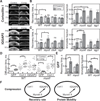
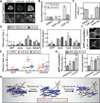
Cell-shape changes associated with processes like cytokinesis and motility proceed on several-second timescales but are derived from molecular events, including protein-protein interactions, filament assembly, and force generation by molecular motors, all of which occur much faster [1-4]. Therefore, defining the dynamics of such molecular machinery is critical for understanding cell-shape regulation. In addition to signaling pathways, mechanical stresses also direct cytoskeletal protein accumulation [5-7]. A myosin-II-based mechanosensory system controls cellular contractility and shape during cytokinesis and under applied stress [6, 8]. In Dictyostelium, this system tunes myosin II accumulation by feedback through the actin network, particularly through the crosslinker cortexillin I. Cortexillin-binding IQGAPs are major regulators of this system. Here, we defined the short timescale dynamics of key cytoskeletal proteins during cytokinesis and under mechanical stress, using fluorescence recovery after photobleaching and fluorescence correlation spectroscopy, to examine the dynamic interplay between these proteins. Equatorially enriched proteins including cortexillin I, IQGAP2, and myosin II recovered much more slowly than actin and polar crosslinkers. The mobility of equatorial proteins was greatly reduced at the furrow compared to the interphase cortex, suggesting their stabilization during cytokinesis. This mobility shift did not arise from a single biochemical event, but rather from a global inhibition of protein dynamics by mechanical-stress-associated changes in the cytoskeletal structure. Mechanical tuning of contractile protein dynamics provides robustness to the cytoskeletal framework responsible for regulating cell shape and contributes to cytokinesis fidelity.
Copyright © 2015 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Engl W, Arasi B, Yap LL, Thiery JP, Viasnoff V. Actin dynamics modulate mechanosensitive immobilization of E-cadherin at adherens junctions. Nat Cell Biol. 2014;16:587–594. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

