Limited mitochondrial permeabilization causes DNA damage and genomic instability in the absence of cell death
- PMID: 25702873
- PMCID: PMC4352766
- DOI: 10.1016/j.molcel.2015.01.018
Limited mitochondrial permeabilization causes DNA damage and genomic instability in the absence of cell death
Erratum in
- Mol Cell. 2015 Jun 4;58(5):900
Abstract
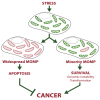
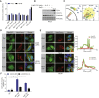
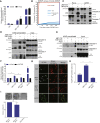
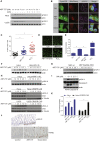
During apoptosis, the mitochondrial outer membrane is permeabilized, leading to the release of cytochrome c that activates downstream caspases. Mitochondrial outer membrane permeabilization (MOMP) has historically been thought to occur synchronously and completely throughout a cell, leading to rapid caspase activation and apoptosis. Using a new imaging approach, we demonstrate that MOMP is not an all-or-nothing event. Rather, we find that a minority of mitochondria can undergo MOMP in a stress-regulated manner, a phenomenon we term "minority MOMP." Crucially, minority MOMP leads to limited caspase activation, which is insufficient to trigger cell death. Instead, this caspase activity leads to DNA damage that, in turn, promotes genomic instability, cellular transformation, and tumorigenesis. Our data demonstrate that, in contrast to its well-established tumor suppressor function, apoptosis also has oncogenic potential that is regulated by the extent of MOMP. These findings have important implications for oncogenesis following either physiological or therapeutic engagement of apoptosis.
Copyright © 2015 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
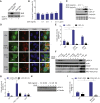


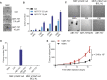
Comment in
-
Life after MOMP.Mol Cell. 2015 Apr 16;58(2):199-201. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2015.03.035. Mol Cell. 2015. PMID: 25884366 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Berardo M.D., Elledge R.M., de Moor C., Clark G.M., Osborne C.K., Allred D.C. bcl-2 and apoptosis in lymph node positive breast carcinoma. Cancer. 1998;82:1296–1302. - PubMed
-
- Colell A., Ricci J.E., Tait S., Milasta S., Maurer U., Bouchier-Hayes L., Fitzgerald P., Guio-Carrion A., Waterhouse N.J., Li C.W. GAPDH and autophagy preserve survival after apoptotic cytochrome c release in the absence of caspase activation. Cell. 2007;129:983–997. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

