Brain changes associated with thromboxane receptor antagonist SQ 29,548 treatment in a mouse model
- PMID: 25703023
- PMCID: PMC4478107
- DOI: 10.1002/jnr.23578
Brain changes associated with thromboxane receptor antagonist SQ 29,548 treatment in a mouse model
Abstract
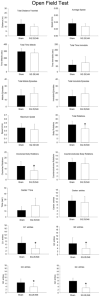
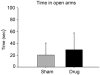
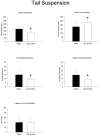
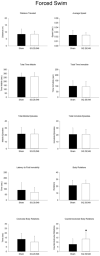
The purpose of this study was to characterize behavioral and physiological effects of a selective thromboxane (TP) receptor antagonist, SQ 29,548, in the C57Bl/6 mouse model. At 6 months of age, male mice were given either sham or drug i.p. injections for 3 days at a dose of 2 mg/kg each day. On the day after the final injection, mice were subjected to behavioral testing before brain collection. Left hemisphere hippocampi were collected from all mice for protein analysis via Western blot. Right brain hemispheres were fixed and embedded in gelatin and then serially sectioned. The sections were immunostained with anti-c-Fos antibodies. Prostaglandin analysis was performed from remaining homogenized brain samples, minus the hippocampi. Injection of SQ 29,548 decreased selective brain prostaglandin levels compared with sham controls. This correlated with robust increases in limbic-region c-Fos immunoreactivity in the SQ 29,548-injected mice. However, drug-treated mice demonstrated no significant changes in relevant hippocampal protein levels compared with sham treatments, as determined from Western blots. Surprisingly, injection of SQ 29,548 caused mixed changes in parameters of depression and anxiety-like behavior in the mice. In conclusion, the results indicate that administration of peripheral TP receptor antagonists alters brain levels of prostanoids and influences neuronal activity, with only minimal alterations of behavior. Whether the drug affects neurons directly or through a secondary pathway involving endothelium or other tissues remains unclear.
Keywords: anxiety; c-Fos; depression; thromboxane; thromboxane receptor.
© 2015 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Neuroprotective effects of thromboxane receptor antagonist SQ 29,548 after pilocarpine-induced status epilepticus in mice.Epilepsy Res. 2020 Feb;160:106277. doi: 10.1016/j.eplepsyres.2020.106277. Epub 2020 Jan 16. Epilepsy Res. 2020. PMID: 32036236
-
The role of prostaglandin E and thromboxane-prostanoid receptors in the response to prostaglandin E2 in the aorta of Wistar Kyoto rats and spontaneously hypertensive rats.Cardiovasc Res. 2008 Apr 1;78(1):130-8. doi: 10.1093/cvr/cvm112. Epub 2007 Dec 18. Cardiovasc Res. 2008. PMID: 18093985
-
Endogenous prostaglandin endoperoxides and prostacyclin modulate the thrombolytic activity of tissue plasminogen activator. Effects of simultaneous inhibition of thromboxane A2 synthase and blockade of thromboxane A2/prostaglandin H2 receptors in a canine model of coronary thrombosis.J Clin Invest. 1990 Oct;86(4):1095-102. doi: 10.1172/JCI114813. J Clin Invest. 1990. PMID: 2145320 Free PMC article.
-
Thromboxane receptor blockade (SQ 29,548) in group B streptococcal toxin challenge in young lambs.Pediatr Res. 1994 May;35(5):571-9. Pediatr Res. 1994. PMID: 8065840
-
Aspects of the thromboxane receptor system.Gen Pharmacol. 1995 May;26(3):463-72. doi: 10.1016/0306-3623(94)00183-n. Gen Pharmacol. 1995. PMID: 7789718 Review.
Cited by
-
Cyclooxygenase inhibition attenuates brain angiogenesis and independently decreases mouse survival under hypoxia.J Neurochem. 2021 Jul;158(2):246-261. doi: 10.1111/jnc.15291. Epub 2021 Feb 25. J Neurochem. 2021. PMID: 33389746 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Andoh T, Nishikawa Y, Yamaguchi-Miyamoto T, Nojima H, Narumiya S, Kuraishi Y. Thromboxane A2 induces itch-associated responses through TP receptors in the skin in mice. The Journal of investigative dermatology. 2007;127(8):2042–2047. - PubMed
-
- Aschbacher K, Roepke SK, von Kanel R, Mills PJ, Mausbach BT, Patterson TL, Dimsdale JE, Ziegler MG, Ancoli-Israel S, Grant I. Persistent versus transient depressive symptoms in relation to platelet hyperactivation: a longitudinal analysis of dementia caregivers. Journal of affective disorders. 2009;116(1-2):80–87. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Belzung C, Griebel G. Measuring normal and pathological anxiety-like behaviour in mice: a review. Behavioural brain research. 2001;125(1-2):141–149. - PubMed
-
- Berk M, Plein H. Platelet supersensitivity to thrombin stimulation in depression: a possible mechanism for the association with cardiovascular mortality. Clinical neuropharmacology. 2000;23(4):182–185. - PubMed
-
- Bousser MG, Amarenco P, Chamorro A, Fisher M, Ford I, Fox K, Hennerici M, Mattle HP, Rothwell PM Investigators PS. The Prevention of cerebrovascular and cardiovascular Events of ischemic origin with teRutroban in patients with a history oF ischemic strOke or tRansient ischeMic attack (PERFORM) study: baseline characteristics of the population. Cerebrovascular diseases. 2009;27(6):608–613. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

